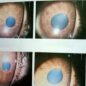
Hey there, fellow science enthusiasts! Have you ever wondered why our pupils dilate after an eye injury? Well, get ready to dive into the fascinating world of ophthalmology as we explore the science behind dilated pupils. Our eyes are incredible organs, constantly adapting to our surroundings and helping us make sense of the world. But when an injury occurs, things can get a little complicated. In this blog post, we’ll break down the causes and effects of pupil dilation after an eye injury, giving you a deeper understanding of this intriguing phenomenon. So, grab your lab coat and let’s get started!
What Are Dilated Pupils?
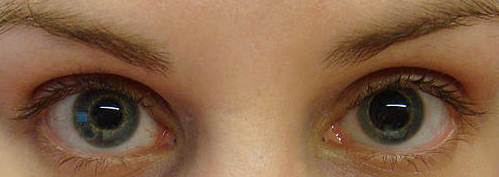
When an eye injury occurs, one of the common responses is dilated pupils. This happens because the eyes become more sensitive to light when they are inflamed. The dilation of the pupils serves as a protective mechanism, allowing less light to enter the injured eye. It helps reduce further irritation and discomfort that could be caused by excessive exposure to bright lights. This response is a natural way for the body to try and shield the injured eye, giving it time to heal and recover. Although dilated pupils may initially be concerning, they generally indicate that the body is responding appropriately to the injury. However, it is still crucial to seek medical attention to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment for a speedy recovery.
Dilated pupil after an eye injury can serve as a crucial indicator of potential damage to the eye or the surrounding tissues. When faced with an eye injury, it is imperative to be aware that the dilation of the pupil can signify more than just a superficial concern. Rather, it may indicate underlying issues that warrant immediate attention and medical intervention. Dilated pupils following an eye injury should never be taken lightly, as they can be indicative of traumatic changes within the eye structure. These changes could potentially involve damage to the retina, optic nerves, or other vital components of the eye. Furthermore, the dilation of the pupil may also point towards injuries affecting the surrounding tissues, such as the muscles or nerves responsible for controlling pupil size. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize dilated pupils as an important sign demanding prompt medical evaluation and treatment after an eye injury occurs. By reacting swiftly and seeking appropriate care, one can ensure the best possible outcomes for their eye health and overall well-being.
All in all, it is crucial to remain vigilant about the presence of dilated pupils after an eye injury. The dilation of the pupils can serve as a crucial indicator that further medical attention is necessary. By promptly recognizing and addressing this symptom, individuals can ensure that the appropriate diagnostic measures are taken to accurately identify and treat any underlying conditions or complications. Neglecting to seek medical attention may result in delayed treatment, potentially leading to further damage or impairments. Therefore, it is paramount to prioritize the monitoring and prompt evaluation of dilated pupils following an eye injury, as this will contribute to securing the best possible outcome for the affected individual.
Causes of Pupil Dilation Following an Eye Injury
When it comes to the topic of a dilated pupil after an eye injury, one potential cause that should be considered is damage to the muscle fibers surrounding the pupil. This damage can lead to the paralysis of these muscles, preventing them from contracting as they normally would. Such paralysis subsequently results in pupil dilation. The dilation of the pupil occurs because without the ability to contract, the muscles are unable to regulate the size of the pupil appropriately. Consequently, the pupil remains dilated, potentially causing discomfort and affecting vision. Therefore, it is crucial to address any possible damage to the muscle fibers surrounding the pupil when examining cases of a dilated pupil after an eye injury. By doing so, medical professionals can better understand and provide appropriate treatment for this condition.
Dilated pupil after an eye injury is a common occurrence, often caused by direct nerve damage. In such cases, the communication between the brain and the eye is disrupted, leading to a loss of control over the pupil’s constriction. This results in the pupil remaining dilated and unable to respond to changes in light. Consequently, the injured individual may experience difficulties with adjusting to different lighting conditions, as their pupil fails to constrict as it should. This condition can be distressing and may affect one’s vision. It is important to seek medical attention promptly to assess the extent of the injury and determine the appropriate treatment to alleviate this issue.
Thereafter, it is evident that the development of a dilated pupil after an eye injury is a complex response that involves various factors. The inflammation occurring in or around the eye as a result of the injury ultimately exerts increased pressure on the muscles responsible for controlling pupil dilation. As a consequence, this physiological reaction takes place as the body attempts to protect and heal itself. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of this phenomenon aids in the diagnosis and treatment of eye injuries, ensuring appropriate care to prevent further complications. Thus, it is crucial for both medical professionals and individuals experiencing such injuries to be aware of the correlation between inflammation, increased pressure, and pupil dilation. By addressing these factors promptly and effectively, potential long-term consequences can be minimized, facilitating a speedy recovery and preserving optimal visual function.
Effects of Dilated Pupils on Vision
When it comes to eye injuries, one common symptom to watch out for is a dilated pupil. This condition, where the pupil appears larger than usual, can be indicative of a problem within the eye. Not only can it be a result of an injury, but it can also contribute to vision problems. Therefore, if you notice a dilated pupil after an eye injury, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. By addressing the underlying issue and receiving proper treatment, you can increase the chances of restoring your vision and preventing any further complications.
After sustaining an eye injury, one of the possible outcomes is a dilated pupil. This condition significantly alters the way light enters the eye, subsequently affecting vision. Specifically, depth perception is notably decreased, making it challenging to accurately perceive distances. Additionally, the ability to focus on distant objects becomes compromised. These effects, accompanied by the dilated pupil after an eye injury, create a situation where the injured individual experiences difficulty in perceiving depth and focusing on objects that are far away.
When experiencing an eye injury, one common issue that can arise is a dilated pupil. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible to address this condition. Over time, if left untreated, the dilation can worsen, which can lead to more serious problems. These may include blurred vision, double vision, or difficulty reading small print. It is crucial to understand the potential consequences of a dilated pupil after an eye injury and take appropriate action to prevent further complications. Seeking prompt medical intervention is key in addressing this matter effectively.
Additionally, it is crucial to understand that any delay in seeking immediate medical attention after an eye injury or the observation of a dilated pupil can potentially lead to severe, long-term damage to one’s vision. The dilation of the pupil could be an indication of a more serious underlying issue that should not be taken lightly. By promptly consulting a medical professional, one can ensure that any necessary treatments or interventions are taken as soon as possible, potentially preventing further complications and preserving their visual health. Remember, when it comes to eye trauma, time is of the essence, and swift action can make all the difference in maintaining optimal eye function for years to come.
How Is Pupil Dilation Diagnosed?
When faced with a dilated pupil after eye injury, eye care professionals approach the situation with careful consideration. They begin by reviewing the patient’s medical history, seeking any relevant information that could aid in the diagnosis. This includes previous eye injuries, underlying conditions, and medications that may have an impact. Afterward, a thorough eye exam is conducted, meticulously examining the affected eye for any signs of trauma or damage. In addition, the professionals assess the symptoms associated with the dilation, such as blurred vision, light sensitivity, or pain. By taking a comprehensive approach to understanding the dilated pupil after eye injury, eye care professionals can effectively diagnose the issue at hand and proceed with appropriate treatment options.
When experiencing a dilated pupil after an eye injury, it is important to undergo a comprehensive eye exam. This examination will encompass various crucial assessments to understand the condition better. The eye exam might entail carefully checking for signs of swelling or redness in the eye, which could indicate inflammation or trauma. Additionally, assessing vision clarity and conducting visual acuity tests will provide valuable insights into the extent of the injury. Furthermore, determining whether there is any damage to the iris, responsible for controlling the size of the pupil, is pivotal in understanding the underlying cause of the dilation. By conducting a thorough eye exam with a focus on these essential aspects, healthcare professionals can gather essential information to diagnose and develop an appropriate treatment plan for individuals who have experienced a dilated pupil after an eye injury.
When dealing with a dilated pupil after an eye injury, it is crucial for the clinician to employ various assessment techniques to determine the cause and severity of the condition. In addition to a comprehensive examination, the clinician may employ a light to evaluate how the pupil responds to light stimuli, carefully measuring its size and shape. This allows them to gather valuable information that can aid in the diagnosis and treatment process. Furthermore, if deemed necessary, imaging tests like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans can be utilized to rule out more serious underlying conditions. These advanced diagnostic tools provide a detailed visualization of the internal structures of the eye, helping the clinician to identify any potential complications or damage caused by the injury. By combining these assessment techniques and tests, medical professionals can ensure a thorough evaluation of a dilated pupil after an eye injury, leading to appropriate and timely interventions for the patient’s wellbeing.
Finally, it is crucial for an individual who has experienced an eye injury to seek immediate medical attention in order to prevent further complications. By taking these steps, an eye care professional can carefully examine the dilated pupil and conduct a thorough assessment to identify any potential underlying causes or additional damage. This critical information will allow the professional to create a personalized treatment plan that may involve medication, surgery, or other appropriate interventions to address the specific condition affecting the dilated pupil. Acting swiftly is of utmost importance in ensuring the best possible outcome and regaining optimal eye health. Therefore, those who experience a dilated pupil following an eye injury should not hesitate to consult with a trusted eye care professional who can provide the necessary guidance and care needed for a successful recovery.
How Is a Dilated Pupil Treated?
When an individual suffers from a dilated pupil after an eye injury, there are various treatment options available that involve a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. This condition, which occurs when the pupil fails to constrict properly in response to light, can be particularly concerning. However, with the right approach, it is possible to manage and improve this condition. Medications such as eye drops or ointments can be prescribed to help control the dilation of the pupil and reduce discomfort. In addition to medication, lifestyle changes may also play a crucial role in the recovery process. Protecting the injured eye from bright lights and wearing sunglasses can offer relief and prevent further damage. Moreover, it is important to avoid activities that may strain the eyes, such as excessive screen time or reading in dim lighting conditions. By following these recommendations, individuals can take proper care of their dilated pupil after an eye injury and work towards a healthier and more comfortable recovery.
When it comes to dealing with dilated pupil after an eye injury, medications such as atropine, pilocarpine, and scopolamine can provide much-needed relief. These drugs have proven to be effective in reducing the dilation of the pupil and helping individuals recover from their injury. Atropine, pilocarpine, and scopolamine work by directly targeting the muscles that control the pupil’s size, allowing them to relax and return to normal function. By doing so, they not only alleviate discomfort but also promote a faster healing process. Overall, these medication options offer a reliable solution for managing dilated pupils post-eye injury, providing patients with the opportunity to regain comfort and normalcy in their daily lives.
In the context of dilated pupil after an eye injury, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in mitigating the severity of dilation symptoms. One effective measure is reducing exposure to bright lights, as excessive light can exacerbate the condition and cause discomfort. By avoiding intense sources of light, individuals can minimize the strain on their already injured eye and alleviate symptoms such as sensitivity and pain. Moreover, wearing sunglasses outdoors can provide additional protection and aid in managing the dilation. By shielding the eyes from harmful UV rays and bright sunlight, sunglasses create a more comfortable environment for the injured eye to heal. These lifestyle modifications, when adopted consistently, can help individuals regain some control over their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Besides avoiding activities that could potentially cause further eye injury or strain on the eye, it is crucial to take additional measures to minimize the risk of exacerbating symptoms of dilation, especially after experiencing an eye injury. This may include wearing protective eyewear when engaging in sports or activities with potential eye hazards, such as home improvement projects or contact sports. Additionally, it is important to follow any specific instructions provided by healthcare professionals, such as avoiding bright lights or excessive screen time, which can contribute to eye strain. By taking these precautions and being mindful of one’s actions, individuals can support the healing process and reduce the chances of further complications associated with a dilated pupil after an eye injury.
Understanding the Role of Neurotransmitters in Eye Injury-Related Pupil Dilation
When it comes to understanding why a dilated pupil occurs after an eye injury, the release of neurotransmitters emerges as the critical factor. These tiny chemical messengers play a crucial role in initiating the process of pupil dilation. Following an eye injury, the body’s response is to release neurotransmitters, which in turn trigger the expansion of the pupil. This reaction occurs as a protective mechanism, aiming to allow more light into the eye, assisting with visibility and ensuring the injured eye is able to properly assess its surroundings. The release of these neurotransmitters acts as a natural response to an injury, demonstrating the complex and intricately designed ways our bodies protect and heal themselves.
When an eye injury occurs, it can cause a disruption in the autonomic nervous system, which regulates various involuntary functions of the body. This interruption leads to the release of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells. Consequently, one of the notable effects of this disruption is the dilation of the pupil. The pupil is the black circular opening in the center of the eye that controls the amount of light entering the eye. Typically, the autonomic nervous system plays a crucial role in controlling the size of the pupil, but when there is a lack of input from this system due to an eye injury, it can result in an abnormal dilation of the pupil, a condition known as mydraisis. This response to the injury is an involuntary and automatic physiological reaction aimed at protecting the eye from further harm. Therefore, when individuals experience an eye injury that leads to a dilated pupil, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to assess and treat any underlying damage or complications.
Additionally, it is crucial to recognize that pupil dilation in the context of an eye injury is not purely a consequence of trauma alone. While trauma can certainly cause pupil dilation, it is essential to consider other factors that may contribute to this condition. Stress and anxiety, for instance, can also lead to pupil dilation, highlighting the complex nature of this physiological response. Furthermore, underlying conditions such as diabetes or hypertension can affect pupil dilation, even in the absence of trauma. Therefore, when examining an individual with dilated pupils after an eye injury, it is imperative to take into account these various factors to ensure accurate assessment and appropriate treatment options.
Psychological Factors Affecting Pupil Dilation After an Eye Injury
When it comes to the occurrence of a dilated pupil after an eye injury, one crucial psychological factor that cannot be overlooked is stress. The impact of stress on the human body is multifaceted, and its effects on pupil dilation should not be underestimated. In cases where an individual is under significant stress, their pupils may instinctively dilate as a response. However, this instinctive reaction can potentially aggravate the injury even further, leading to increased inflammation and complications. The intricate connection between stress and pupil dilation in the context of eye injuries highlights the importance of managing stress levels to ensure proper healing and recovery. By recognizing this crucial relationship, individuals can take proactive measures to address their stress levels, ultimately promoting a more favorable healing process free from unnecessary complications.
When it comes to dilated pupil after an eye injury, anxiety can play a significant role in exacerbating its effects. The impact of anxiety on the body is known to trigger the release of hormones like cortisol, which, unfortunately, can result in pupil dilation. This dilation, when coupled with an eye injury, can further worsens the inflammation already present, potentially causing long-term damage to the eye. Therefore, managing anxiety becomes crucial in preventing the adverse consequences of dilated pupil after an eye injury.
The dilated pupil after an eye injury is influenced by another significant psychological factor – fear. When we experience fear or sense a potential threat, our natural response is to have our pupils dilate, enabling us to gather more detailed information about our surroundings. However, this reaction can have negative consequences on the inflamed eye and may even lead to vision complications due to its impact on intraocular pressure.
However, while it is important to consider the physical factors that contribute to pupil dilation after an eye injury, it is equally crucial not to overlook the potential psychological impact. The potential trauma associated with such an injury cannot be disregarded, as it can have a significant influence on the dilation of the pupil. Psychological distress resulting from the injury may trigger a fear response, leading to increased pupil dilation and potentially exacerbating the complications associated with the initial injury. Therefore, it is imperative that healthcare professionals take a holistic approach when treating patients with dilated pupils after an eye injury, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects to ensure comprehensive and effective care.
Possible Complications From Dilated Pupils After an Eye Injury
Dilated pupils after an eye injury can be a cause for concern as they may result in various complications. One such complication is blurred vision, where the affected individual experiences difficulty in seeing objects clearly. This can greatly affect their daily activities and overall quality of life. Additionally, eyestrain may occur, causing discomfort and fatigue in the eye muscles due to prolonged focusing. Headaches are another common complication related to dilated pupils after an eye injury, often accompanied by eye discomfort and sensitivity to light. These headaches can range from mild to severe and may persist until the pupil returns to its normal size. Furthermore, increased light sensitivity is frequently observed, making it challenging for the individual to tolerate bright light, which can lead to discomfort and further strain on the eyes. Hence, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly when experiencing dilated pupil after an eye injury in order to prevent or address these potential complications.
After sustaining an eye injury, an individual may experience a dilated pupil, which can lead to a range of complications. These complications can be further exacerbated by the muscles surrounding the eye not returning to their previous strength or alignment. As a consequence, the affected individual may suffer from double vision and misalignment of the eyes. These difficulties can significantly impact their daily life and overall visual function, causing frustration and discomfort. Seeking immediate medical attention is crucial to address the issue and prevent any long-term consequences. Healthcare professionals specializing in eye injuries can provide appropriate treatment to alleviate the symptoms and facilitate a prompt recovery.
Similarly, it is crucial for individuals who experience dilated pupils as a result of an eye injury to promptly seek medical attention. By doing so, they can ensure that any potential long-term effects are minimized. Seeking immediate medical care allows for prompt diagnosis and treatment, which is essential in achieving the best possible outcome. Medical professionals possess the expertise and resources to accurately assess the severity of the injury, develop a tailored treatment plan, and provide necessary interventions to prevent further damage to the eye. With early intervention, individuals can receive the appropriate care and commence treatment promptly, enabling a quicker recovery process and potentially reducing any lasting consequences. Thus, it is imperative for those experiencing dilated pupils after an eye injury to prioritize seeking medical attention urgently, enabling them to initiate the necessary steps towards optimal healing and restoration of vision.
Prevention Tips for Avoiding Intense and Prolonged Pupillary Response Following an Eye Injury
In order to avoid experiencing intense and prolonged pupillary response after sustaining an eye injury, it is crucial for individuals to take the necessary preventive measures. One effective way to minimize the risk of such injuries is by always wearing protective eyewear when participating in activities that have a potential for eye injury, such as sports or hazardous work environments. By investing in and utilizing proper eye protection, individuals can significantly decrease the chances of damaging their eyes and subsequently suffering from dilated pupils as a result. This proactive approach not only safeguards against potential harm but also promotes a responsible and cautious attitude towards eye health and safety.
When dealing with a dilated pupil after an eye injury, it is imperative to prioritize the safety and protection of the affected individual. In addition to seeking immediate medical attention, it is also crucial to ensure that any protective eyewear worn conforms to the required safety standards. This ensures that not only is the injured eye safeguarded from further harm, but also that proper care is taken to prevent any potential complications associated with a dilated pupil. Moreover, it is essential that the protective eyewear is properly fitted to the individual’s face and eyes, as this guarantees maximum protection. By adhering to these precautions and guidelines, one can effectively mitigate the risks associated with a dilated pupil after an eye injury, promoting a safe and healthy recovery.
Read also: Intraocular Lenses for Cataract Surgery
Finally, in the event of an eye injury, it is of utmost importance to seek immediate medical attention to mitigate the likelihood of a dilated pupil resulting from the injury. This prompt response plays a critical role in ensuring a speedy recovery and minimizing any potential long-term damage. By promptly consulting a medical professional, individuals can receive the necessary treatment and care tailored specifically to their injury, thus increasing the chances of a positive prognosis. Delaying medical attention in such cases can exacerbate the injury and potentially lead to complications that might have been preventable. Thus, by prioritizing immediate medical intervention, individuals can effectively safeguard their eye health and take the necessary steps towards recovery.