Hey there, curious readers! Have you ever wondered if there’s a way to predict or even detect strokes before they strike? Well, get ready for an eye-opening discussion on a fascinating topic – the link between pupil dilation and stroke! It turns out that our eyes can offer valuable clues about our overall health, including the potential risk of experiencing a stroke. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the science behind pupil dilation and its connection to strokes, and we’ll break down the important things you need to know. So, grab your favorite beverage, sit back, and get ready to expand your knowledge on this intriguing subject!
Introduction to Pupil Dilation and Stroke
Pupil dilation, a reflexive response in the eye, is often a crucial indicator of various neurological conditions. One such condition that has drawn attention is strokes. During a stroke, pupils may indeed dilate, but it is essential to clarify the underlying causes. Typically, pupil dilation occurs when light is shined into the eye, triggering a reflexive response from the brain processing specific stimuli. However, during a stroke, the dilated pupils observed are usually unequal and unresponsive to light stimuli, signifying an urgent medical concern. Monitoring pupil dilation in stroke patients is therefore vital for healthcare professionals to assess and manage the severity of the condition promptly.
When a person experiences a stroke, a medical emergency resulting from an interruption of blood flow to the brain, there are various physiological changes that can occur. One such change is the dilation of the pupils, which is attributed to the neurological damage caused by the sudden lack of blood flow. During a stroke, the brain’s normal functioning is disrupted, leading to a cascade of events that can affect different parts of the body. The autonomic nervous system, responsible for regulating pupil size, can be affected, leading to the enlargement of the pupils. This dilation can be an indicator for healthcare professionals in diagnosing a stroke and understanding the extent of neurological damage. Therefore, observing dilated pupils can be crucial in identifying and treating this life-threatening condition promptly.
Additionally, it is crucial to recognize that dilated pupils can indeed be a sign of a stroke. This information may prove vital in preventing further damage or even saving a life. By understanding that excessive pupil dilation can indicate an impending stroke or a stroke that has already occurred, individuals can be empowered to seek immediate medical attention. Recognizing this important symptom and acting swiftly can greatly increase the chances of receiving appropriate treatment and improving outcomes. Therefore, it is imperative to be aware of the potential link between pupil dilation and strokes, as staying informed and alert can make all the difference in one’s health and well-being.
What is Pupil Dilation?
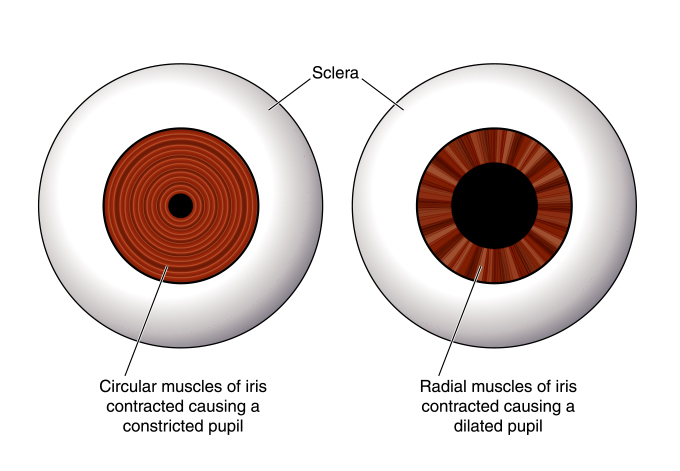
During a stroke, it is important to examine whether pupils dilate or not as this can provide crucial information about the severity of the condition. Pupil dilation refers to the widening of the black center of the eye, known as the pupil. This occurs as a result of the muscles around it either constricting or relaxing, depending on the amount of light entering the eye. Specifically, in the context of a stroke, observing pupil dilation can be indicative of significant physiological changes occurring in the brain. By monitoring whether the pupils dilate or fail to respond appropriately during a stroke, medical professionals can gain insight into the extent of damage and help determine the most appropriate course of treatment for the patient.
During a stroke, pupil dilation is a crucial factor that can serve as a significant indicator of potential neurological damage. The dilation of pupils during a stroke has been widely recognized as a relevant characteristic to determine whether an individual is experiencing a stroke or not. This phenomenon holds immense importance in the medical field, as it allows healthcare professionals to promptly identify and diagnose strokes by simply assessing the dilation of a patient’s pupils. By studying the extent of pupil dilation, medical practitioners are able to ascertain the severity of the stroke and make informed decisions about appropriate treatment. This understanding of how pupils dilate during a stroke has revolutionized the way strokes are detected, enabling rapid intervention and potentially life-saving outcomes.
Thus, assessing pupil dilation within minutes of a suspected stroke is crucial in determining the occurrence of a stroke and the extent of brain damage. By closely monitoring pupil size, healthcare professionals can quickly identify whether a stroke has occurred, allowing for immediate intervention to minimize further damage. The dilation of the pupils during a stroke provides valuable insight into the severity of the condition, guiding the selection of appropriate treatments. Prompt assessment of pupil dilation is essential for ensuring timely and effective care, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Therefore, the observation of dilated pupils during a suspected stroke can serve as a vital indicator, enabling healthcare providers to take proactive measures in reducing potential brain damage and enhancing the overall management of the patient.
What is a Stroke?
A stroke is a medical emergency that demands urgent attention as it occurs when blood supply to the brain is abruptly blocked or interrupted. This interruption leads to a deprivation of oxygen and nutrients to the brain cells, which can result in severe consequences. One notable aspect during a stroke that raises curiosity among individuals is whether or not pupils dilate. It is understandable why this question arises, as pupils dilating can often indicate possible medical issues. However, when it comes to strokes, pupils may or may not dilate, and this variation depends on various factors. Therefore, it is crucial to seek immediate medical assistance during a stroke, rather than solely relying on pupil dilation as an indicator.
During a stroke, when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, it can have detrimental effects on different regions of the brain. This interruption in blood supply can cause parts of the brain to begin deteriorating, resulting in a range of symptoms that are dependent on which specific area of the brain is affected. One critical aspect that may be impacted during a stroke is the dilation of pupils. Pupil dilation is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which can be compromised by the lack of blood flow to the brain. This can lead to unequal or non-reactive pupil sizes, known as anisocoria. Furthermore, since the pupils are responsible for regulating the amount of light entering the eye, changes in their dilation can affect vision and visual perception. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor pupil dilation during a stroke as it can serve as an important indicator of potential brain damage and help guide medical interventions.
During a stroke, several symptoms can manifest, some of which are difficulty speaking or understanding speech, paralysis or numbness on one side of the body, confusion, and vision problems such as dilated pupils. When it comes to the question of whether pupils dilate during a stroke, it is essential to consider the overall condition of the individual. While dilated pupils are not a direct and consistent symptom of a stroke, they can occur in certain cases. The dilation of the pupils during a stroke may be linked to other factors such as an increase in blood pressure or a disruption in the autonomic nervous system. However, it is important to note that pupils dilating alone cannot be solely relied upon as an indication of a stroke. The occurrence of dilated pupils should always be considered in conjunction with other prevalent symptoms such as difficulty speaking or paralysis. Therefore, when assessing a potential stroke, a comprehensive evaluation of all symptoms is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and prompt medical intervention.
Thus, recognizing the signs of a stroke early is crucial in order to promptly administer medical treatment and mitigate long-term damage and disability. While there may be various symptoms associated with a stroke, such as facial drooping, difficulty speaking, and weakness or numbness on one side of the body, the dilation of pupils can also serve as a vital indicator. Promptly identifying this particular sign can expedite the necessary medical intervention, enabling healthcare professionals to provide immediate care and potentially minimize the extent of brain damage. By raising awareness about the significance of pupil dilation during a stroke, individuals can be better equipped to respond quickly and seek appropriate medical attention. This proactive approach can ultimately improve the chances of a more favorable outcome for stroke patients, highlighting the importance of early recognition and treatment in safeguarding their overall well-being.
How are Pupil Dilation and Stroke Connected?
Pupil dilation is a well-documented phenomenon that frequently accompanies strokes, serving as a significant indicator of the condition. During a stroke, the disruption of nerve pathways responsible for controlling eye movements leads to dilated pupils that are unable to react to changes in light. This occurrence, often observed in stroke patients, underscores the importance of monitoring pupil responses as part of diagnostic procedures. The inability of dilated pupils to regulate their reaction to light serves as a crucial signifier, allowing medical professionals to promptly identify and intervene in cases of stroke. Understanding the connection between strokes and pupil dilation can aid in recognizing the occurrence and severity of such an event, ultimately enhancing the prospects for timely treatment and improved patient outcomes.
During a stroke, the pupil dilation is a significant indicator that can help detect the presence of brain damage. Pupils dilate as a result of this medical emergency, whether it be caused by an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. This dilation serves as a clear sign of the level of severity of the brain damage incurred. It is important to note that pupil dilation may occur in both mild and severe cases of stroke, further emphasizing its significance as an indicator. By assessing whether or not pupils dilate during a stroke, medical professionals can gather crucial information about the extent of brain damage and determine appropriate treatment protocols.
When it comes to the topic of whether pupils dilate during a stroke, it is important to consider the significance of pupil dilation as an early indication of this potentially life-threatening event. Pupil dilation has been found to be one of the first signs that a stroke has occurred, which should not be taken lightly. This enlargement of the pupils serves as an alarming signal, suggesting that something serious might have transpired in the brain. Therefore, it is crucial to understand that when pupils dilate during a stroke, it requires immediate attention and prompt medical intervention. Recognizing this symptom and seeking timely medical assistance can greatly aid in ensuring appropriate treatment and potentially improving the outcome for the individual affected by a stroke.
Also, it is crucial to note that pupil dilation tests play a significant role in diagnosing strokes and determining appropriate treatment for recovery. When a stroke occurs, the brain’s blood supply is interrupted, leading to various neurological symptoms. As the severity of a stroke can vary, medical professionals rely on assessments such as pupil dilation tests to gauge the extent of damage and make informed decisions about the course of action. By observing pupil size and responsiveness, doctors can identify potential complications, monitor progress, and tailor treatments accordingly. Consequently, these tests provide valuable insights into the condition and guide healthcare providers in delivering optimal care to stroke patients. Understanding whether or not pupils dilate during a stroke is just one piece of the puzzle that contributes to the overall assessment and management of this critical medical emergency.
Symptoms of Pupil Dilation During a Stroke
During a stroke, it is not uncommon for a person to experience pupil dilation as a potential symptom. This occurrence can be attributed to the blockage of an artery within the brain. Specifically, when this blockage occurs, it causes the pupil of the affected eye to widen beyond its usual size. Pupil dilation serves as a significant indication of a stroke and can be used as a visual cue to identify potential medical emergencies. Recognizing this symptom promptly can facilitate immediate medical attention, which is crucial in improving the chances of a positive outcome. Hence, understanding that pupils may dilate during a stroke aids in the early detection and timely intervention needed to mitigate the potential severity of the condition.
During a stroke, it is important to note that pupil dilation can occur, which may be accompanied by a range of other symptoms. These symptoms could include dizziness, confusion, difficulty speaking and understanding language, as well as paralysis or numbness in one side of the body and sudden changes in vision. When discussing the topic of “do pupils dilate during a stroke,” it is crucial to be aware of these additional signs that can manifest alongside pupil dilation. It is essential to approach this topic with a serious tone, acknowledging the gravity of the situation and the significance of recognizing these symptoms as potential indicators of a stroke.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs and symptoms of a stroke and understanding the potential role of pupil dilation in its detection is crucial for timely intervention. Should there be any suspicion that someone might be experiencing a stroke, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention. While it is not an absolute indication, pupil dilation can serve as a potential red flag during a stroke event. By being aware of this potential symptom, individuals can play a proactive role in identifying strokes when they occur, allowing for prompt medical intervention, which greatly increases the chances of a positive outcome. Remember, every second counts when it comes to strokes, so familiarize yourself with the signs and act swiftly if you suspect a stroke by paying attention to numerous indicators, such as pupil dilation, to ensure the best possible care and recovery.
Benefits of Early Detection of Pupil Dilation During a Stroke
Early detection of pupil dilation during a stroke is of utmost importance when it comes to providing timely medical intervention and minimizing potential long-term damage caused by the stroke. Understanding whether pupils dilate during a stroke is crucial as it allows healthcare professionals to identify and respond promptly to this significant symptom. By closely monitoring any changes in pupil size, medical experts can quickly recognize the onset of a stroke and take immediate action, ensuring that patients receive the appropriate treatment as soon as possible. The dilation of pupils during a stroke serves as an important indicator, enabling medical professionals to initiate interventions that can potentially save lives and prevent further complications. Hence, recognizing this specific symptom promptly allows for rapid medical intervention, leading to better outcomes and reducing the potential negative impact of strokes.
The question of whether pupils dilate during a stroke is an important one, as it can provide significant insights into the severity and extent of stroke symptoms. The detection of pupil dilation holds valuable information that can assist doctors in determining the most appropriate course of action. By closely monitoring changes in pupil size, medical professionals can gather crucial data to better understand the condition of a stroke patient. This information, coupled with other diagnostic tools and assessments, allows doctors to make informed decisions regarding immediate interventions and long-term treatment plans. Thus, the ability to ascertain whether or not pupils dilate during a stroke plays a pivotal role in optimizing patient care and improving outcomes.
By monitoring for pupil dilation, healthcare professionals can swiftly and accurately identify the occurrence of a stroke in an individual, enabling them to promptly take necessary steps to safeguard the patient’s well-being and initiate necessary treatments. During a stroke, the brain experiences a sudden interruption in its blood supply, leading to various symptoms including vision impairment. The ability to observe changes in pupil size offers a valuable tool in identifying this medical emergency. Pupil dilation, where the pupils become larger than normal, can be indicative of a stroke. By promptly recognizing this symptom, healthcare professionals can ensure that immediate interventions are implemented to prevent further damage and potentially save lives. The monitoring of pupil dilation serves as an essential diagnostic tool that enables healthcare professionals to rapidly respond and provide the necessary care for stroke patients, emphasizing the importance of continuous observation in stroke management.
Furthermore, it is imperative to understand the critical role that pupil dilation plays in the early detection of strokes. It has been widely observed that during a stroke, pupils often exhibit dilation. This key indication serves as a red flag, prompting immediate medical attention and intervention. Consequently, recognizing the early signs of pupil dilation in stroke patients provides healthcare professionals with a valuable window of opportunity to initiate timely treatment, ultimately preventing further brain tissue death. By addressing the underlying causes of the stroke at its earliest stages, medical experts can effectively minimize the risk of permanent disability or even death. Thus, understanding the relationship between pupil dilation and strokes is pivotal in ensuring the best possible outcome for patients.
Risk Factors for Pupil Dilation Caused by a Stroke
During a stroke, there are several risk factors that can contribute to pupil dilation. High blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease are the main culprits in this regard. These conditions have the potential to cause the arteries in the brain to become narrow or blocked. When this happens, blood flow to the brain is significantly reduced, ultimately leading to a stroke. It is important to note that the dilation of pupils during a stroke can be influenced by these underlying medical conditions. By understanding the relationship between these risk factors and pupil dilation, medical professionals can better assess and diagnose strokes. Overall, it is crucial to recognize the impact of high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease on pupil dilation during a stroke, as they play a significant role in determining the course of medical treatment and care.
High blood pressure and diabetes play significant roles in the occurrence of pupil dilation during a stroke, posing potential risks to individuals. High blood pressure, a condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels, is closely linked to an increased likelihood of experiencing an ischemic stroke, which is the most prevalent type of stroke. Ischemic strokes occur when an artery supplying blood to the brain becomes blocked or narrowed, interrupting proper blood flow. Interestingly, pupil dilation during a stroke is commonly associated with this particular type. Similarly, diabetes, a condition marked by high blood sugar levels, also contributes to the possibility of artery blockage. When blood sugar levels are unregulated, the risk of artery obstruction rises, impeding the flow of oxygenated blood to the brain and potentially triggering pupil dilation. The occurrence of dilated pupils during a stroke necessitates an understanding of these underlying health conditions and their implications. Remaining vigilant regarding high blood pressure and diabetes is crucial in managing these risk factors and reducing the chances of experiencing stroke-related complications.
Finally, it is crucial to recognize that individuals with cardiovascular disease are particularly vulnerable to pupillary dilation during a stroke, exacerbating the gravity of their condition. Their heightened susceptibility to aneurysms and arterial blockages further increases the risk of dilation in the pupils. Moreover, the presence of cardiovascular ailments, such as coronary heart disease, hampers the circulation of oxygenated blood throughout the body, adding another layer of susceptibility to pupillary dilation during a stroke event. This intricate relationship between cardiovascular disease and pupillary response underscores the urgent need for comprehensive medical attention in order to promptly identify and address potential strokes in individuals who already suffer from cardiovascular ailments. It is imperative that medical professionals remain vigilant and proactive in their approach towards strokes in these vulnerable populations, ensuring timely intervention and potentially saving lives.
Treatments for Pupil Dilation Resulting from a Stroke
When considering the question of whether pupils dilate during a stroke, it becomes essential to adopt a multi-step approach in the treatment process. The first crucial step is to determine the underlying cause of the dilation. In order to do so, medical professionals may conduct various tests to identify potential aneurysms, blood clots, or other blockages within the blood vessels in the brain. By thoroughly examining these factors, healthcare providers can gain a better understanding of how pupils may dilate during a stroke and tailor their treatment strategy accordingly.
During a stroke, it is common for pupils to dilate as a result of changes in blood flow and pressure within the brain. This dilation of the pupils can be an important indicator for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating a stroke. Once the cause of the pupil dilation is identified, treatment may involve taking medications to reduce blood pressure or surgery to remove blockages that are preventing proper circulation. Depending on the severity of the stroke, rehabilitation therapies may also be recommended to improve motor and cognitive function affected by the stroke. Therefore, understanding whether or not pupils dilate during a stroke plays a crucial role in identifying the condition and implementing appropriate interventions.
In conclusion, monitoring changes in the size or activity of a patient’s pupils over time following a stroke is of utmost importance. The dilation of the pupils can serve as a potential indicator of a more serious condition developing, highlighting the need for immediate medical attention. By closely observing any variations in the pupils’ size or responsiveness, healthcare professionals can promptly intervene and provide the necessary treatments to mitigate further complications. Timely detection of these changes is crucial in ensuring the well-being and recovery of stroke survivors, promoting optimal patient care and reducing the risk of potentially harmful consequences. Therefore, healthcare providers must remain vigilant and proactive in monitoring pupils’ dilation as part of their comprehensive stroke assessment protocols, prioritizing the well-being and safety of their stroke-stricken individuals.
Tips to Prevent the Risk of Experiencing a Stroke
When considering the question “do pupils dilate during a stroke,” it is important to note that pupils do not typically dilate as a direct result of having a stroke. However, there are effective measures one can take to minimize the risk of experiencing a stroke. First and foremost, prioritizing a healthy lifestyle is crucial. This includes engaging in regular exercise and adopting a balanced diet. By maintaining a physically active routine and consuming nutritious foods, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of suffering from a stroke. While the dilation of pupils may not be indicative of a stroke, taking preventive actions is paramount for overall well-being.
In addition to understanding whether pupils dilate during a stroke, it is crucial to prioritize overall health by monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Keeping these levels within a healthy range is essential for a well-functioning cardiovascular system. Regularly checking these vital signs and seeking medical advice when needed is imperative. By doing so, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent strokes and other cardiovascular complications. If prescribed by a healthcare professional, it is important to diligently take any medications provided to help control blood pressure and cholesterol levels. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and reducing the risk of strokes.
Read also: Best Eye Drops For Scratched Cornea
Additionally, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of experiencing a stroke. By avoiding smoking and excessive drinking, you can significantly decrease the chances of suffering from this life-threatening condition. It is well-known that these behaviors have detrimental effects on our health and can lead to a myriad of health issues, including strokes. Therefore, taking the necessary preventative measures, such as adopting a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress levels, can play a pivotal role in safeguarding against strokes. Remember, our overall well-being is in our hands, and by making conscious choices and adopting healthy habits, we can actively protect ourselves from the dangers associated with strokes.