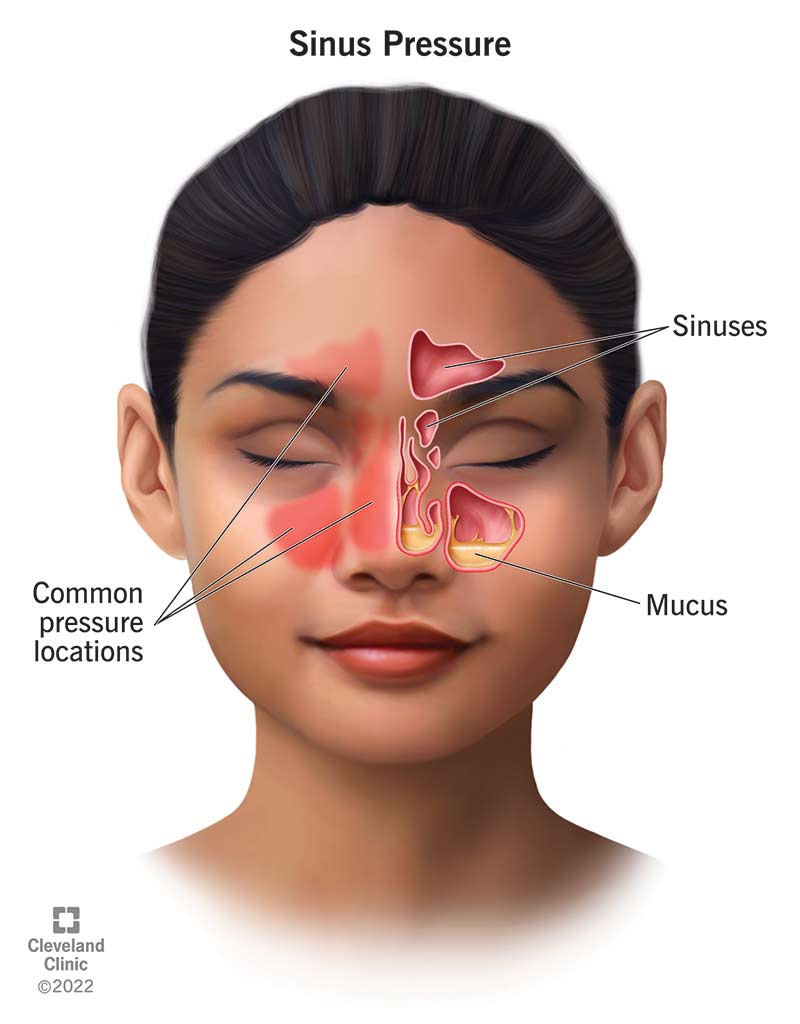
Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps are non-cancerous growths that occur in the maxillary sinus, a hollow space located in the cheekbones. These polyps can lead to various symptoms and may require medical attention. In the realm of medical coding, specifically the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Edition (ICD-10), specific codes exist to accurately document and categorize these conditions.
Defining Maxillary Sinus Polyps
Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps represent benign growths originating from the mucous membrane lining the maxillary sinus, one of the four paired sinuses situated within the facial bones. These growths often manifest as soft, painless protrusions and are typically associated with chronic inflammation of the sinus lining. While the precise etiology of maxillary sinus polyps remains a subject of research, factors such as allergies, infections, or chronic sinusitis are commonly implicated in their development.
Maxillary sinus polyps vary in size and can obstruct the sinus passages, leading to a range of symptoms. Patients may experience nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, facial pain or pressure, and a reduced sense of smell. Although these growths are generally non-cancerous, their impact on a patient’s quality of life necessitates proper diagnosis and, subsequently, accurate coding for effective medical management.
Beyond the discomfort they cause, maxillary sinus polyps can contribute to recurring sinus infections and complicate pre-existing conditions such as asthma. Therefore, a thorough understanding of these polyps, from their clinical presentation to their appropriate ICD-10 coding, is vital for healthcare professionals involved in the diagnosis, treatment, and documentation of patients with this condition.
ICD-10 Overview
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Edition (ICD-10), serves as a comprehensive and globally recognized system for classifying and coding diseases, disorders, and other health-related conditions. Introduced by the World Health Organization (WHO), the ICD-10 provides a standardized language that facilitates communication among healthcare professionals, researchers, and administrators worldwide.
Within the ICD-10, the coding system allocates alphanumeric codes to specific medical conditions, allowing for precise documentation and classification. In the case of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps, the relevant code falls under the broader category of J33, which covers various nasal polyps and their locations. This systematic approach ensures consistency in medical recordkeeping, promoting accurate statistical analysis, research, and epidemiological studies.
The ICD-10 system is structured hierarchically, with codes becoming more specific as one navigates through the alphanumeric sequence. This hierarchical arrangement allows healthcare providers to capture nuances in diagnoses, such as distinguishing between the right and left maxillary sinus when coding for nasal polyps. Specifically, for right-sided maxillary sinus polyps, the code J33.01 is assigned, offering a level of granularity that is crucial for precise medical documentation and billing.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, so does the ICD system. The transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 represented a significant advancement in capturing the complexity of medical conditions, enabling more accurate representation of diagnoses and facilitating improved patient care through enhanced coding specificity. It is imperative for healthcare professionals to stay abreast of updates and changes in the ICD system to ensure the accurate and up-to-date representation of conditions such as Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps in clinical records.
J33.0 – Polyp of Nasal Cavity
The primary ICD-10 code for documenting maxillary sinus polyps, among other nasal polyps, is J33.0. This code falls within the broader category of diseases of the respiratory system, facilitating a systematic and standardized approach to coding for these conditions. The assignment of J33.0 allows healthcare professionals to classify and communicate the presence of nasal polyps, including those specifically located in the maxillary sinus.
Within the expansive realm of the J33.0 code, healthcare providers can further refine their documentation to denote the precise anatomical location of the polyps. In the case of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps, a more specific code, J33.01, is assigned. This additional level of detail is crucial in conveying the exact location of the polyps within the nasal cavity, enabling a more accurate representation of the patient’s condition.
J33.0 serves as a linchpin in the coding process, acting as a gateway to a comprehensive understanding of nasal polyps while also providing the flexibility to capture specific nuances related to location. This systematic approach ensures that the nuances of each patient’s case are accurately reflected in their medical records, contributing to more effective communication among healthcare professionals and supporting informed decision-making in the realm of patient care.
Moreover, the assignment of J33.0 plays a pivotal role in statistical analysis and epidemiological studies. By using a standardized coding system, healthcare data can be aggregated, allowing researchers and public health officials to gain insights into the prevalence, incidence, and trends associated with nasal polyps, including those in the right maxillary sinus. This, in turn, aids in the development of evidence-based guidelines and strategies for managing and treating these conditions.
Right Maxillary Sinus Specificity
Within the intricate web of medical coding, precision is paramount. To further refine the documentation of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps, healthcare professionals utilize additional digits in the ICD-10 code. The primary code, J33.01, not only signifies the presence of nasal polyps but specifically pinpoints their location in the right maxillary sinus. This level of specificity is invaluable for clinicians, coders, and other healthcare stakeholders as it offers a nuanced understanding of the patient’s condition.
The utilization of these additional digits aids in creating a comprehensive and accurate patient profile, essential for tailoring effective treatment plans. Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps may present with distinct challenges compared to their counterparts in other nasal cavities, and the specificity in coding reflects these unique considerations. This precision becomes particularly crucial when assessing the effectiveness of treatments or understanding the potential impact on adjacent structures in the right maxillary sinus.
In a broader context, the detailed coding of right maxillary sinus involvement contributes to a more granular database for research purposes. Researchers can delve into the specific characteristics and outcomes associated with right-sided polyps, fostering a deeper understanding of the condition’s complexities. As healthcare continues to move towards personalized medicine, these nuanced codes become integral tools for tailoring interventions to individual patient needs.
Associated Symptoms
Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps often manifest with a spectrum of symptoms that can significantly impact a patient’s daily life. These symptoms include nasal congestion, a feeling of pressure or fullness in the face, and potential headaches. As healthcare professionals navigate the ICD-10 coding system, understanding the associated symptoms becomes pivotal in comprehensive patient care.
Accurate coding of these symptoms not only aids in diagnosis but also contributes to a more holistic representation of the patient’s health status. For instance, a patient reporting chronic facial pain associated with right maxillary sinus polyps may prompt further investigation into the potential impact on their quality of life and overall well-being. By incorporating these symptoms into the coding process, healthcare providers can address not only the anatomical aspects of the condition but also its functional and symptomatic dimensions.
Moreover, the inclusion of associated symptoms in coding is essential for monitoring the progression of the disease and assessing the efficacy of interventions. As patients undergo treatment, changes in symptoms can be tracked through the corresponding ICD-10 codes, providing valuable insights into the dynamic nature of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps and guiding adjustments in the therapeutic approach. This holistic coding approach ensures that the entire clinical picture is captured, promoting a more patient-centered and effective healthcare strategy.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps often involves a multifaceted approach, with diagnostic procedures playing a crucial role in confirming the presence of these growths. Healthcare providers commonly employ imaging studies, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, to visualize the sinus cavities and identify any abnormalities. In the coding landscape, the utilization of such diagnostic tools aligns with the need for precision.
ICD-10 codes serve as a bridge between clinical assessments and administrative recordkeeping. For instance, if a CT scan reveals right maxillary sinus polyps, the assigned J33.01 code substantiates the diagnostic findings and provides a standardized language for communication among healthcare professionals. The meticulous integration of diagnostic information into coding ensures that the nuances of the diagnostic process are accurately reflected in the patient’s medical record.
The incorporation of diagnostic procedures into coding also facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the severity and extent of right maxillary sinus polyps. By documenting not only the presence of polyps but also their characteristics and distribution, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to address the specific needs of the patient. This alignment between diagnostics and coding contributes to a more nuanced and patient-centric approach to managing Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, the management of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps encompasses various treatment modalities, ranging from medical interventions to surgical procedures. ICD-10 codes play a pivotal role in documenting these diverse treatment approaches. For instance, the administration of corticosteroids may be coded using specific pharmacy codes, while surgical interventions, such as polypectomy, may involve additional procedure codes.
Accurate coding not only reflects the diversity of treatment options but also allows for the monitoring of treatment outcomes over time. As healthcare providers adjust treatment plans based on the patient’s response, the corresponding ICD-10 codes evolve, providing a dynamic and comprehensive representation of the patient’s therapeutic journey. This coding precision is instrumental in evaluating the effectiveness of various interventions and refining treatment strategies for optimal patient outcomes.
Furthermore, coding facilitates communication between healthcare providers and other stakeholders involved in the patient’s care, including pharmacists, insurers, and researchers. The standardized language provided by ICD-10 codes ensures that everyone involved in the patient’s healthcare journey has access to accurate and up-to-date information, fostering collaborative decision-making and continuity of care.
Challenges in Coding
While the ICD-10 system offers a robust framework for coding medical conditions, challenges can arise in the coding of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps. One of the primary challenges lies in the need to accurately distinguish between right and left sinus involvement. The anatomical specificity required in coding demands meticulous attention to clinical documentation to ensure precision.
Healthcare coders must navigate through a plethora of information in medical records to accurately assign the appropriate codes. This challenge becomes particularly pronounced in cases where patients may have bilateral sinus involvement or when the documentation lacks clarity regarding the laterality of the polyps. Regular training and communication between healthcare providers and coders are essential to address these challenges and maintain coding accuracy.
Additionally, the evolving nature of medical knowledge and technology introduces new diagnostic and treatment modalities, necessitating updates in coding guidelines. Staying informed about changes in the coding landscape is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure accurate representation of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps and other conditions in the ever-evolving field of healthcare documentation.
Coding for Recurrent Cases
Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps can exhibit a recurrent nature, requiring healthcare professionals to consider the long-term management of the condition. In such cases, ICD-10 codes play a vital role in documenting the chronicity and recurrence of the polyps. For example, the addition of a seventh character in the code (e.g., J33.01A for initial encounter, J33.01D for subsequent encounters) denotes the stage of treatment and the recurrence status.
This nuanced coding not only assists in tracking the patient’s medical history but also informs healthcare providers about the trajectory of the condition. Recurrent Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps may necessitate adjustments in treatment plans, and accurate coding ensures that these changes are reflected in the patient’s records. Additionally, the coding of recurrent cases contributes valuable data to epidemiological studies, enhancing our understanding of the factors influencing the recurrence of maxillary sinus polyps.
ICD-10 Coding for Complications
In some instances, Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps may lead to complications, such as chronic sinusitis or exacerbation of pre-existing respiratory conditions. When coding for these complications, healthcare professionals utilize additional ICD-10 codes to capture the complexity of the patient’s clinical presentation. For example, codes from the J32 category may be used to indicate chronic sinusitis.
Accurate coding for complications is crucial for several reasons. It provides a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health status, aids in the coordination of care among different specialties, and ensures that insurance claims accurately reflect the resources expended in managing complex cases. Furthermore, this coding approach contributes to the identification of potential risk factors and informs preventive measures to mitigate complications associated with Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps.
Coding in Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
As healthcare continues its digital transformation, the integration of ICD-10 codes into Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is a pivotal aspect of modern healthcare documentation. The seamless incorporation of these codes into EHRs streamlines communication among healthcare professionals, enhances data accuracy, and supports evidence-based decision-making.
In EHRs, ICD-10 codes serve as the linchpin that connects various aspects of patient care. From diagnostic procedures and treatment plans to outcomes and follow-up care, the use of standardized codes ensures consistency and clarity in the documentation. This not only facilitates intra-institutional communication but also enables interoperability, allowing patient information to be shared securely across different healthcare settings.
Moreover, the inclusion of ICD-10 codes in EHRs enhances the efficiency of administrative processes, such as billing and insurance claims. By automating these processes, healthcare organizations can reduce errors, improve reimbursement timelines, and allocate resources more effectively. The integration of coding into EHRs represents a synergistic relationship between technology and healthcare, fostering a more connected and efficient approach to managing conditions like Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps in the contemporary healthcare landscape.
Reimbursement and Insurance Claims
Accurate ICD-10 coding is instrumental in the financial aspects of healthcare, particularly in the context of reimbursement and insurance claims. The specificity offered by ICD-10 codes, especially in distinguishing between right and left maxillary sinus involvement in the case of polyps (J33.01), ensures that healthcare providers can appropriately bill for their services.
Insurance companies rely on these codes to assess the medical necessity of procedures and treatments, determine coverage eligibility, and process claims efficiently. A well-documented and precisely coded record, including the right ICD-10 codes, strengthens the provider’s case for reimbursement, reducing the likelihood of claim denials or delays.
Furthermore, accurate coding aligns with the principles of ethical billing, ensuring that healthcare services are billed appropriately based on the complexity and specificity of the patient’s condition. This process is critical for maintaining the financial health of healthcare institutions and supporting ongoing patient care and operational needs.
Patient Education
ICD-10 codes can also play a role in patient education. While these codes may seem like technical jargon to the layperson, they provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to engage patients in understanding their condition. By explaining the assigned codes, healthcare professionals can empower patients to be more informed about their health, treatment options, and potential complications.
Patient education becomes particularly relevant in chronic conditions like Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps, where a collaborative approach between healthcare providers and patients is essential. Understanding the ICD-10 codes associated with their condition allows patients to actively participate in discussions about their treatment plans, prognosis, and long-term management strategies.
Moreover, as patients become more familiar with the codes, they can contribute to more accurate self-reporting of symptoms during healthcare visits, fostering a more transparent and collaborative relationship with their healthcare providers.
Ongoing Research and Code Updates
The world of medicine is dynamic, with continuous advancements in research, diagnostics, and treatment modalities. ICD-10 codes serve as a vital tool for researchers and epidemiologists to analyze trends, outcomes, and factors influencing conditions such as Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps.
Regular updates to the ICD-10 system ensure that it stays current with the evolving landscape of medical knowledge. Healthcare professionals need to stay informed about these updates to accurately document and code for conditions, contributing to the ongoing refinement of medical classification systems.
The synergy between research and coding not only enhances our understanding of diseases and their management but also paves the way for future improvements in healthcare delivery. The insights gained from coded data contribute to evidence-based medicine, driving advancements in treatments, preventive strategies, and healthcare policies.
In conclusion, the role of ICD-10 codes in the context of Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps is multifaceted and indispensable. From facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment documentation to supporting reimbursement processes and ongoing research endeavors, these codes are the backbone of modern healthcare documentation.
Read also: Dupilumab Chronic Rhinosinusitis Without Nasal Polyps
Healthcare providers, coders, and researchers must work collaboratively to ensure the precision of coding, recognizing its impact on patient care, institutional operations, and the broader landscape of medical knowledge. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the strategic use of ICD-10 codes remains an essential element in delivering effective, patient-centered care for conditions like Right Maxillary Sinus Polyps.