When it comes to corneal transplants, there are several different types to choose from. Each type has its own benefits and risks, and the decision on which one to choose can be overwhelming. Corneal transplants are typically used to treat vision problems such as corneal scarring, keratoconus, and other corneal diseases. In this blog post, we will break down the different types of corneal transplants and help you understand which one may be right for you. From traditional full-thickness corneal transplants to newer techniques such as DMEK and DSAEK, we will provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision about your eye health.
-
Introduction to corneal transplants and their purpose
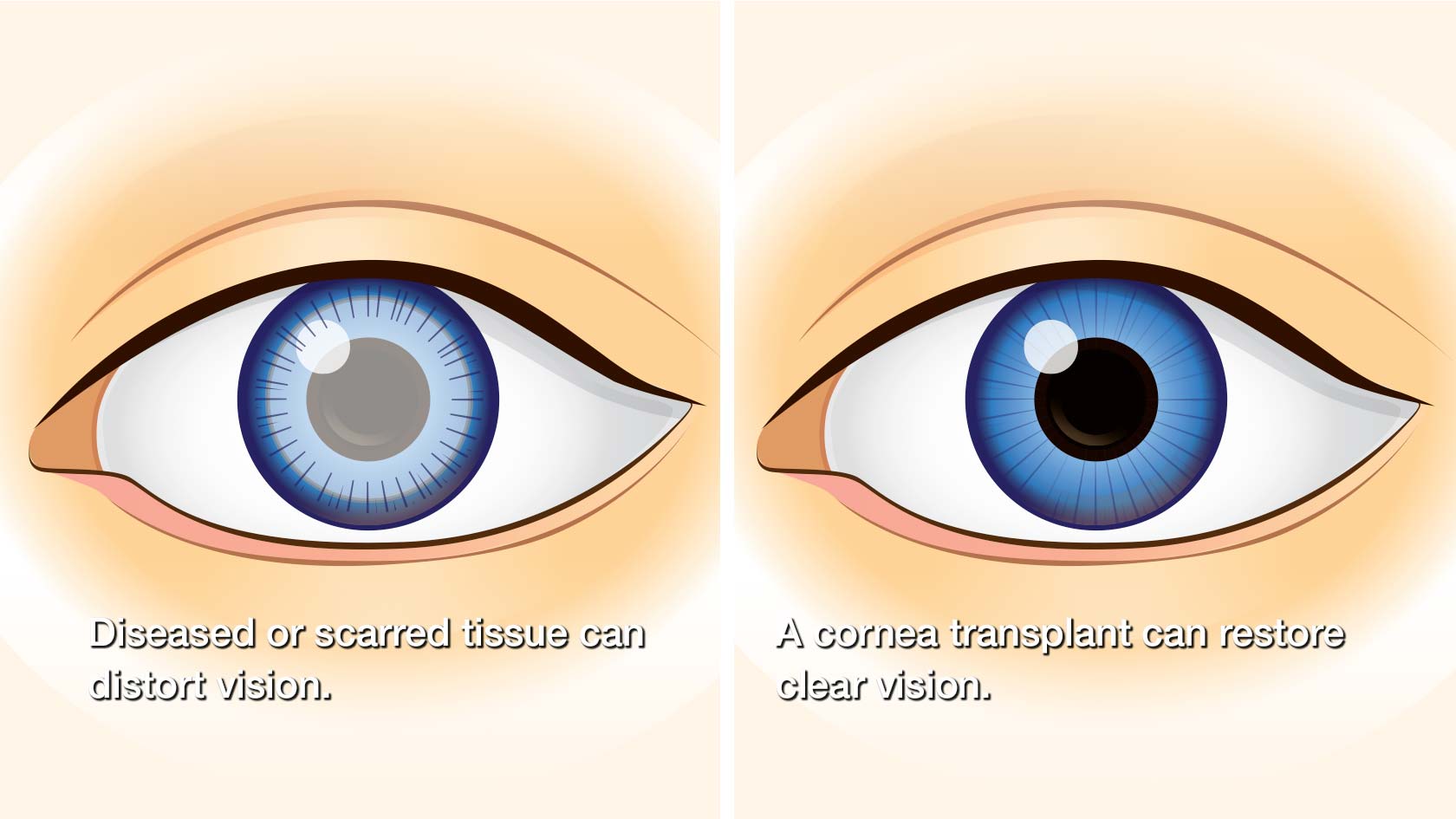
Corneal transplants are surgical procedures that replace damaged or diseased corneas with healthy donor corneas. The cornea, which is the clear, dome-shaped front part of the eye, plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, allowing us to see clearly. However, various factors such as infections, injuries, degenerative diseases, or genetic conditions can cause corneal damage, leading to vision impairment or loss.
The purpose of corneal transplants is to restore vision and improve the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from corneal issues. By replacing the damaged cornea with a healthy one, these procedures aim to correct vision problems, reduce pain or discomfort, and enhance the overall functioning of the eye.
There are different types of corneal transplants, each tailored to address specific corneal conditions. The choice of transplant procedure depends on the extent and nature of the corneal damage, as well as the patient’s individual needs and circumstances. Understanding the various types of corneal transplants is crucial in determining which one is right for you or your loved one.
In the following sections, we will explore the different types of corneal transplants in detail, discussing their procedures, benefits, and potential risks. By gaining insight into these options, you will be better equipped to have informed discussions with your ophthalmologist or eye specialist, ultimately making the best decision for your vision health and well-being.
-
Overview of the cornea and its role in vision
The cornea is a vital component of our visual system, playing a crucial role in our ability to see the world around us. Located at the front of the eye, it acts as a protective outer layer and helps to focus light onto the retina, which then sends signals to the brain for image processing.
Composed of transparent tissue, the cornea is responsible for approximately two-thirds of the eye’s refractive power. This means that any irregularities or abnormalities in its shape or structure can significantly impact our vision. Conditions such as corneal dystrophies, infections, injuries, or degeneration can lead to corneal damage, resulting in blurred vision, discomfort, and even vision loss.
When conservative treatments fail to provide relief or restore visual acuity, corneal transplantation may be considered. This surgical procedure involves the removal of the damaged or diseased cornea and replacing it with a healthy cornea from a donor. However, it is essential to understand that not all corneal transplants are the same, and the specific type chosen depends on the individual’s condition and needs.
There are several different types of corneal transplants, each targeting specific layers or portions of the cornea. The most common types include penetrating keratoplasty (full-thickness corneal transplant), deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (partial thickness), Descemet’s stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK), and Descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK).
Penetrating keratoplasty involves replacing the entire cornea and is typically performed in cases of severe corneal damage or scarring. Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty, on the other hand, targets the outer and middle layers of the cornea while preserving the innermost layer, the endothelium. This technique is often employed when the endothelium is healthy, but the outer layers are affected.
DSAEK and DMEK are newer procedures that specifically address endothelial dysfunction. In DSAEK, a thin layer of posterior cornea containing the endothelium is transplanted, while in DMEK, only the endothelium and a thin layer of Descemet’s membrane are replaced. These techniques offer quicker recovery times and better visual outcomes for patients with endothelial disorders.
It is crucial to consult with an experienced ophthalmologist or corneal specialist to determine the most suitable corneal transplant option based on the individual’s condition, visual needs, and overall health. Understanding the role of the cornea in vision and the different transplant options available empowers patients to make informed decisions regarding their eye health and visual well-being.
-
Full-thickness corneal transplant (penetrating keratoplasty)
A full-thickness corneal transplant, also known as penetrating keratoplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves replacing the entire thickness of the damaged or diseased cornea with a healthy donor cornea. This type of corneal transplant is typically recommended for patients with extensive corneal damage or diseases that affect the entire cornea, such as advanced keratoconus, corneal scarring, or corneal dystrophies.
During the procedure, the surgeon removes a central portion of the patient’s cornea and replaces it with a donor cornea. The donor cornea is carefully selected based on factors such as tissue compatibility and quality. The new cornea is then stitched into place using tiny sutures.
Full-thickness corneal transplant is a major surgery that requires a skilled and experienced ophthalmologist. The procedure is usually performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s preference and the surgeon’s recommendation.
Recovery after a full-thickness corneal transplant can take several months, during which the patient will need to follow strict post-operative care instructions. This may include the use of eye drops, wearing a protective shield, and avoiding activities that could put strain on the eye.
While full-thickness corneal transplant can be highly effective in restoring vision and improving quality of life for patients with severe corneal conditions, it is important to note that there are potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. These may include infection, graft rejection, and astigmatism.
If you are considering a corneal transplant, it is crucial to consult with an ophthalmologist who specializes in corneal diseases and transplant surgeries. They will evaluate your specific condition and determine the most suitable type of corneal transplant for you, whether it is a full-thickness corneal transplant or another type, such as a partial-thickness transplant (DALK or DSEK).
Understanding the different types of corneal transplants and discussing your options with a qualified professional will help you make an informed decision about your eye health and visual restoration.
-
Lamellar corneal transplants: Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty (DSEK) and Descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK)
When it comes to corneal transplants, there are different types to consider, each with their own unique benefits and considerations. Two common types of lamellar corneal transplants are Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty (DSEK) and Descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK).
DSEK involves replacing the innermost layer of the cornea, known as the endothelium, which is responsible for maintaining corneal clarity. This procedure involves removing the unhealthy endothelial cells and replacing them with a thin layer of donor tissue. DSEK offers several advantages, including faster recovery times, reduced risk of rejection, and improved visual outcomes compared to traditional full-thickness transplants. It is particularly beneficial for patients with endothelial dysfunction, such as Fuchs’ dystrophy or corneal edema.
On the other hand, DMEK is a newer technique that involves transplanting only the Descemet’s membrane and endothelium, without the additional tissue layers. This results in a thinner and more anatomically accurate transplant, leading to potentially better visual outcomes and faster recovery times compared to DSEK. DMEK is often preferred for patients with relatively healthy corneas but with endothelial dysfunction. However, it is a more technically demanding procedure and requires greater surgical expertise.
Both DSEK and DMEK are considered minimally invasive compared to full-thickness transplants, as they preserve the majority of the patient’s cornea. This results in reduced surgical risks and complications, as well as faster visual rehabilitation. However, not all patients are suitable candidates for lamellar transplants, and a thorough evaluation by an ophthalmologist is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment option.
In conclusion, lamellar corneal transplants, such as DSEK and DMEK, offer innovative solutions for patients with corneal conditions affecting the endothelial layer. These procedures provide faster recovery times, reduced risk of rejection, and improved visual outcomes compared to traditional full-thickness transplants. Consulting with an experienced eye surgeon will help determine the most suitable transplant option based on individual circumstances and overall ocular health.
-
Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK)
Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK) is a type of corneal transplant that offers a unique approach to treating certain corneal conditions. Unlike other types of corneal transplants that involve replacing the entire cornea, DALK targets only the anterior layers of the cornea while leaving the healthy innermost layer, known as the endothelium, intact.
This procedure is particularly beneficial for patients with conditions that primarily affect the front layers of the cornea, such as keratoconus or corneal scarring. By preserving the endothelium, DALK minimizes the risk of endothelial rejection or failure, which can occur in other types of transplants.
During a DALK procedure, the surgeon carefully removes the damaged or diseased layers of the cornea, leaving behind a healthy inner layer. The donor tissue used in DALK can be sourced from a cornea bank, and it typically includes the outer layers of the cornea, including the epithelium, Bowman’s layer, and stroma.
By selectively replacing only the damaged layers, DALK aims to improve vision and restore the structural integrity of the cornea without compromising the crucial endothelial function. This technique offers several advantages over traditional full-thickness corneal transplants, including a reduced risk of rejection, improved long-term outcomes, and faster visual recovery.
However, it is important to note that not all corneal conditions are suitable for DALK. The decision on the type of corneal transplant is determined by various factors, including the specific condition, its severity, and the individual patient’s needs. Only a qualified ophthalmologist can determine whether DALK is the right choice for a particular case.
In conclusion, DALK is a specialized type of corneal transplant that targets the anterior layers of the cornea while preserving the healthy endothelial layer. It offers unique benefits for patients with specific corneal conditions, but the suitability of this procedure depends on various factors. Consulting with an experienced ophthalmologist is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment option for each individual.
-
Comparison of the different corneal transplant techniques
When it comes to corneal transplants, there are several techniques available, each with its own advantages and considerations. Understanding the differences between these techniques is crucial in determining which one is the most suitable for you.
- Penetrating Keratoplasty (PKP):
This is the traditional and most common technique used in corneal transplantation. It involves replacing the full thickness of the damaged or diseased cornea with a healthy donor cornea. While PKP has a high success rate, it requires a longer recovery period and may have a higher risk of complications such as astigmatism.
- Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (DALK):
DALK is a technique that replaces only the front layers of the cornea, leaving the back layers intact. It is typically used for patients with corneal diseases that primarily affect the outer layers, such as keratoconus. DALK offers several benefits, including reduced risk of tissue rejection and better visual outcomes compared to PKP. However, it requires a high level of surgical expertise.
- Descemet’s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK) and Descemet’s Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK):
These techniques are specifically designed to address diseases affecting the endothelial layer of the cornea. DSEK involves replacing the damaged endothelium and a small portion of the underlying tissue, while DMEK replaces only the endothelium. Both DSEK and DMEK offer faster visual recovery, fewer complications, and better preservation of the recipient corneal tissue compared to PKP. However, they are technically demanding procedures and require a healthy donor endothelium.
- Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Keratoplasty:
This advanced technique utilizes a femtosecond laser to create precise, customized incisions during corneal transplantation. It can be used in conjunction with PKP, DALK, or endothelial keratoplasty techniques to enhance surgical precision and optimize visual outcomes. However, due to the additional technology involved, this technique may come at a higher cost.
Choosing the right corneal transplant technique requires a thorough evaluation of your specific condition, corneal health, and potential risks and benefits associated with each technique. Consulting with an experienced ophthalmologist is essential in determining the most appropriate approach for your individual needs.
-
Factors to consider when choosing the right corneal transplant technique
Choosing the right corneal transplant technique is a crucial decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key factors to keep in mind when making this important choice:
- Underlying condition: The specific condition affecting your cornea will play a significant role in determining the appropriate transplant technique. Different conditions, such as keratoconus, Fuchs’ dystrophy, or corneal scarring, may require different approaches to ensure optimal outcomes.
- Graft availability: The availability of suitable donor corneas may influence the choice of transplant technique. Traditional full-thickness corneal transplants (penetrating keratoplasty) require a full-thickness donor cornea, whereas newer techniques like Descemet’s stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK) or Descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) utilize thinner grafts.
- Recovery time: The recovery time associated with each technique should be taken into account. While some techniques may offer quicker visual recovery, they may also involve a more prolonged healing process. Understanding the expected timeline for each technique can help you plan accordingly.
- Surgical complexity: Different transplant techniques vary in terms of surgical complexity. Some techniques may involve more intricate surgical procedures, which may be associated with a higher risk of complications. It is essential to discuss these risks with your ophthalmologist to make an informed decision.
- Long-term outcomes: Consider the long-term outcomes associated with each technique. Some methods may offer improved visual outcomes or a reduced risk of graft rejection. Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks of each technique can help you weigh your options effectively.
- Surgeon’s expertise: The experience and expertise of your surgeon are crucial factors in determining the success of the transplant. It is important to choose a surgeon who is proficient in the specific technique you are considering and has a track record of successful outcomes.
Remember, your ophthalmologist will play a vital role in guiding you through the decision-making process. They will evaluate your individual circumstances, assess the suitability of different techniques, and help you make an informed choice that aligns with your unique needs and goals.
-
Preparing for a corneal transplant surgery
Preparing for a corneal transplant surgery is an important step in ensuring a successful outcome and a smooth recovery. Before undergoing the procedure, it is crucial to follow certain guidelines and make necessary preparations.
First and foremost, it is essential to have a thorough consultation with your ophthalmologist or corneal specialist. They will evaluate your eye condition, discuss the potential risks and benefits of the surgery, and determine if you are a suitable candidate for a corneal transplant. This consultation will also give you an opportunity to ask any questions you may have and address any concerns.
In the days leading up to the surgery, your doctor may advise you to refrain from wearing contact lenses or using eye makeup. This is to ensure that your eyes are in the best possible condition for the procedure. Additionally, you may be instructed to avoid certain medications that can increase the risk of bleeding or interfere with the healing process.
It is important to arrange for someone to accompany you to the hospital or surgical center on the day of the transplant. As the procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, you will be awake but may feel some discomfort or pressure. Having a trusted companion by your side will provide emotional support and ensure your safety during transportation.
Furthermore, it is crucial to follow any fasting instructions provided by your doctor. Typically, you will be asked to refrain from eating or drinking anything for a certain period of time before the surgery. This is done to minimize the risk of complications during the procedure.
Lastly, make sure to arrange for a comfortable and quiet recovery space at home. Following the surgery, your eye may be covered with a protective shield or patch, and you may experience some discomfort or blurry vision. Having a calm environment to rest and recover will aid in your healing process.
By diligently following these preparation steps, you can optimize your chances of a successful corneal transplant surgery and pave the way for a smooth recovery journey. Remember to closely follow all post-operative instructions provided by your doctor to ensure the best possible outcome for your vision health.
-
Recovery and post-operative care after a corneal transplant
Recovery and post-operative care are crucial aspects of the journey following a corneal transplant. After the surgery, it is normal to experience some discomfort, redness, and blurred vision. It is essential to follow the instructions provided by your ophthalmologist to ensure a successful recovery and to optimize the outcome of the procedure.
The first few days after the transplant are critical, and you may be required to wear an eye patch or shield to protect the eye and prevent any accidental rubbing or scratching. Your doctor will prescribe medications, such as antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops, to help prevent infection and manage inflammation. These drops will need to be used as directed, and it is important not to skip any doses.
During the recovery period, it is vital to avoid any strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or bending over, as this can increase pressure in the eye and potentially jeopardize the success of the transplant. It is also recommended to avoid swimming, hot tubs, and any dusty or dirty environments that could introduce bacteria or irritants into the eye.
Regular follow-up appointments with your ophthalmologist are crucial to monitor the healing process and ensure that the new cornea is functioning well. These appointments will typically involve various tests to assess the vision and the overall health of the eye. It is essential to attend these appointments as scheduled and communicate any concerns or issues you may have.
In addition to the medical aspects of recovery, it is equally important to take care of your overall well-being during this time. Getting enough rest, eating a nutritious diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can all contribute to a smoother recovery process.
Recovering from a corneal transplant can take several months, and the timeline may vary for each individual. It is essential to be patient and follow all the guidelines provided by your healthcare team. With proper care and attention, the chances of a successful transplant and improved vision are significantly enhanced.
-
Success rates and potential complications of corneal transplant surgeries
When considering a corneal transplant surgery, it is essential to understand the success rates and potential complications associated with the different types of procedures. While corneal transplants have become increasingly successful over the years, it is important to weigh the benefits against the risks before making a decision.
One of the most common types of corneal transplant surgeries is penetrating keratoplasty (PK), where the entire central cornea is replaced with a donor cornea. The success rates for PK have improved significantly, with studies showing success rates ranging from 80% to 90%. However, there are potential complications that can arise, such as graft rejection, infection, and astigmatism.
Another type of corneal transplant is endothelial keratoplasty (EK), which involves replacing only the innermost layer of the cornea. This procedure has a higher success rate compared to PK, with success rates exceeding 90%. EK has fewer potential complications, such as a reduced risk of graft rejection and a faster recovery time. However, it is important to note that EK may not be suitable for all patients, as it depends on the condition of the patient’s cornea.
Complications associated with corneal transplant surgeries can vary depending on the individual and the procedure performed. Graft rejection, where the body’s immune system attacks the transplanted cornea, is one of the most common complications. Symptoms of graft rejection include redness, sensitivity to light, and a decrease in vision. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent further damage if graft rejection occurs.
Other potential complications include infection, increased intraocular pressure, astigmatism, and irregular healing of the cornea. It is important to discuss these potential risks with your ophthalmologist and weigh them against the potential benefits of the surgery.
In conclusion, understanding the success rates and potential complications of different corneal transplant surgeries is vital in making an informed decision. Consultation with an experienced ophthalmologist will help determine the most suitable type of corneal transplant for your specific condition, taking into consideration your overall eye health and potential risks involved.
- Conclusion: Making an informed decision about the right corneal transplant for you
In conclusion, making an informed decision about the right corneal transplant for you is crucial to ensure the best possible outcome for your vision and overall eye health. Throughout this article, we have explored the different types of corneal transplants available, including penetrating keratoplasty (PKP), deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK), and endothelial keratoplasty (EK).
Each procedure has its own unique benefits and considerations, depending on the specific condition of your cornea and your individual needs. It is important to consult with an experienced ophthalmologist who specializes in corneal transplantation to evaluate your case thoroughly and recommend the most suitable option for you.
Factors such as the extent of corneal damage, the presence of other eye conditions, and the likelihood of graft rejection should all be taken into account when making this decision. Additionally, your doctor will assess your overall health, age, and lifestyle factors to determine the best approach.
Remember, the goal of any corneal transplant is to restore clear vision and improve the quality of your life. By understanding the different types of corneal transplants and working closely with your ophthalmologist, you can confidently make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs and ensures the best possible outcome.
Ultimately, the success of your corneal transplant relies not only on the expertise of your surgeon but also on your commitment to post-operative care and regular follow-up visits. It is important to adhere to all medication schedules, attend all recommended appointments, and report any changes or concerns promptly.
With the advancements in corneal transplantation techniques and ongoing research, the future holds even more promise for improved outcomes and enhanced visual results. By staying informed and proactive in your decision-making process, you are taking the necessary steps towards achieving optimal eye health and regaining clear vision.
Read also: What does a healthy eyeball look like
We hope this blog post has provided you with valuable insights into the different types of corneal transplants available and helped you understand which one may be the right choice for your specific situation. Making a decision about undergoing a corneal transplant can be daunting, but with knowledge and understanding, you can feel more confident in discussing your options with your healthcare provider. Remember, each individual’s case is unique, and consulting with a qualified professional is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment plan. We wish you the best of luck on your journey towards improved vision and a brighter future.