Hey there! Have you ever heard of antrochoanal polyps? No worries if you haven’t, because today we’re diving into this mysterious condition that affects the nasal passage. Antrochoanal polyps, or ACPs for short, may sound like a mouthful, but understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment is actually quite fascinating. So, whether you’re experiencing some nasal congestion or just a curious soul, this blog post is here to break it all down for you. From its origins to the pesky symptoms it brings along, we’ll cover everything you need to know about ACPs. So, grab a cup of tea, get cozy, and let’s explore the world of antrochoanal polyps together!
What is Antrochoanal Polyp icd-10?
An antrochoanal polyp, also known by its abbreviation ACP, is a harmless growth of tissue that develops within the nasal cavity. This condition falls under the category of antrochoanal polyp icD-10, which refers to the specific coding used for the classification and diagnosis of this particular disorder. An antrochoanal polyp icD-10 code is important in the medical field for standardized communication and classification purposes. By utilizing the antrochoanal polyp icD-10 code, healthcare professionals can accurately identify and document this benign nasal tissue mass, enabling efficient diagnosis and appropriate treatment plans to be implemented.
An antrochoanal polyp is a condition that is typically caused by chronic inflammation of the nasal area and sinuses. This inflammation can be triggered by allergies or other medical conditions. The ICD-10 classification system provides a specific code for this particular condition, enabling healthcare professionals to accurately document and track cases. Antrochoanal polyps can cause various symptoms such nasal obstruction, facial pain, and recurrent infections. These polyps are more commonly seen in children and adolescents, and their growth originates in the maxillary sinus before extending into the nasal cavity. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Antrochoanal polyp (ACP) falls under the category of respiratory system disorders in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), which is a system that assigns codes to various diseases and healthcare diagnoses. The ICD-10 serves to provide a standardized method of classifying medical conditions, facilitating accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. In the case of ACP, this classification system enables healthcare professionals to accurately identify and categorize this specific type of nasal polyp. By utilizing the assigned ICD-10 code, medical practitioners can communicate and share information about ACP in a standardized manner, ensuring consistency and facilitating efficient management of this condition. The comprehensive nature of ICD-10 aids in promoting seamless healthcare services and enhances the overall understanding and treatment of antrochoanal polyps.
Furthermore, having a standardized and specific ICD-10 code for Antrochoanal Polyp, such J34.8, is of utmost importance in the medical field. This code not only facilitates accurate diagnosis and classification of this particular condition but also serves a vital purpose in terms of insurance claims and reimbursement procedures. By using the antrochoanal polyp ICD-10 code, healthcare providers can ensure that they receive fair compensation for the treatments and procedures associated with this condition. It streamlines the process of claiming reimbursement from insurance companies, thus reducing administrative burdens and ensuring a smoother and more efficient healthcare system for both patients and providers alike. With the antrochoanal polyp ICD-10 code in place, healthcare professionals can confidently navigate the complexities of insurance billing and focus more on delivering optimal care to patients.
Causes of Antrochoanal Polyp
Antrochoanal polyps, classified under ICD-10 as J33.8, are non-cancerous growths that develop on the roof of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. These polyps arise as a result of inflammation and the accumulation of secretions within the affected area. They are relatively benign in nature, causing symptoms such as nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, and a reduced sense of smell. Although antrochoanal polyps are not considered dangerous, they can cause significant discomfort and impact the overall quality of life for individuals affected by them. Seeking appropriate medical attention and treatment is important to manage and alleviate the symptoms associated with this condition.
The etiology of antrochoanal polyps remains largely unknown, as researchers have yet to pinpoint the exact cause. However, several contributing factors have been hypothesized, including chronic inflammation, allergies, and sinus cavity infections. Chronic inflammation is believed to play a significant role in the development of these polyps, possibly triggering abnormal growth within the sinus cavities. Additionally, individuals with allergies may be more susceptible to antrochoanal polyps, as the body’s immune response to allergens can lead to persistent inflammation. Furthermore, sinus cavity infections have also been linked to the formation of these polyps, suggesting that recurring or untreated infections may contribute to their development. While the precise cause of antrochoanal polyps is still uncertain, further research and exploration of these potential factors may provide valuable insights into their prevention and treatment.
Thus, it is crucial to recognize and address any underlying structural defects or environmental triggers that may contribute to the development of antrochoanal polyps. By avoiding smoking and seeking treatment for any nasal blockages, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this condition. Taking proactive measures to maintain a healthy nasal passage not only promotes overall well-being but also helps prevent the formation of antrochoanal polyps. Therefore, it is essential to prioritize nasal health and the prevention of potential risk factors to ensure a better quality of life.
Symptoms of Antrochoanal Polyp
Antrochoanal polyps, classified under the ICD-10 code for nasal polyps, are benign growths that typically develop in the nose and sinuses. These growths can lead to several discomforting symptoms. One of the most common signs is nasal obstruction, which can make breathing difficult for individuals affected by this condition. Furthermore, an antrochoanal polyp can also result in a reduced sense of smell, diminishing one’s ability to perceive scents accurately. Another troublesome symptom is postnasal drainage, where excessive mucus and secretions flow down the back of the throat, causing a constant urge to clear the throat or cough. It is essential to recognize and diagnose these symptoms accurately to ensure appropriate medical management and improve the quality of life for those dealing with antrochoanal polyps.
Antrochoanal polyps, a condition covered under ICD-10, can manifest through various symptoms. Alongside the key terms, such polyps often lead to frequent sinus infections, causing significant discomfort. Individuals may experience facial pain and persistent headaches, which can disrupt daily activities and reduce overall quality of life. Additionally, coughing is another potential symptom associated with antrochoanal polyps, further exacerbating the discomfort. Snoring may also become more prevalent in those affected by this condition. As these symptoms persist, it becomes crucial for individuals to seek medical attention and receive an accurate diagnosis to ensure appropriate treatment and relief.
In the context of antrochoanal polyps, it is important to consider the relevant medical coding and classification system known Antrochoanal polyp ic-10. As part of this classification, one notable symptom associated with antrochoanal polyps is a nasal discharge that can vary in color and consistency. The discharge may be clear or discolored and can range from being thick to thin in texture. This specific detail further emphasizes the significance of antrochoanal polyp ic-10 in accurately identifying and documenting this condition. By recognizing such symptoms and utilizing the appropriate coding system, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose and treat patients suffering from antrochoanal polyps.
Thus, it is evident that antrochoanal polyps, classified under the icb-10 code, can be a source of significant discomfort and pain for individuals. These polyps not only obstruct the nasal passage, leading to difficulty in breathing, but they can also create an increase in pressure within the sinuses. As a result, patients may experience discomfort in the face or teeth, further adding to their distress. Understanding the icb-10 classification of antrochoanal polyps allows healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and treat this condition, ensuring that patients receive the necessary care and relief from their symptoms.
Diagnosis of Antrochoanal Polyp
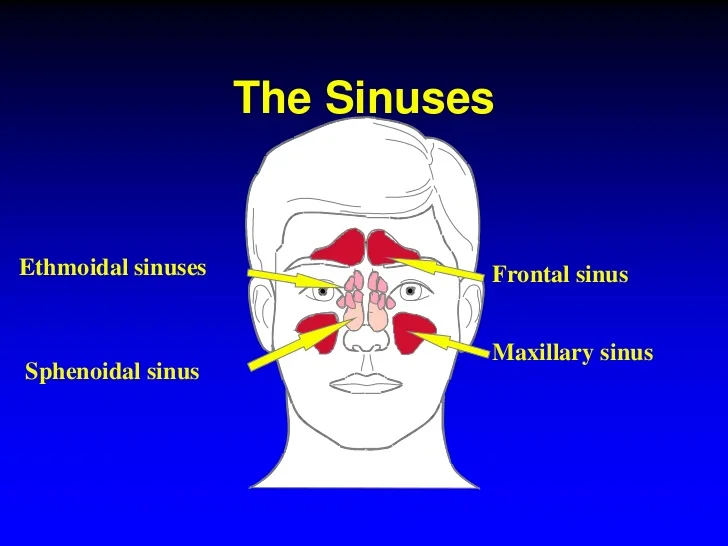
The antrochoanal polyp is a remarkably uncommon and harmless sinonasal tumor. This peculiar growth originates from the mucous membrane of the maxillary antrum, a cavity in the upper jaw, and extends into the nasal cavity, causing a range of symptoms. Although relatively rare, the medical community recognizes the significance of accurately diagnosing and treating this condition. Therefore, having a clear understanding of the antrochoanal polyp’s characteristics and classifying it consistently with the appropriate ICD-10 code is crucial for effective management and patient care.
The diagnosis of an antrochoanal polyp, according to the classification system provided by the International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision (ICD-10), relies heavily on imaging techniques like computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. These advanced imaging methods enable healthcare professionals to accurately identify and characterize the antrochoanal polyp. By utilizing CT scans, doctors can obtain detailed cross-sectional images of the affected area, allowing them to assess the size, location, and extent of the polyp within the nasal cavity. MRI scans, on the other hand, utilize powerful magnets and radio waves to produce high-resolution images that aid in capturing important information about the soft tissues surrounding the polyp. The integration of these imaging techniques is crucial in ensuring an accurate diagnosis and facilitating appropriate treatment planning for patients with antrochoanal polyps, consistent with the guidelines set forth by the antrochoanal polyp ICD-10 classification system.
Next, it is important to note that the identification and proper diagnosis of an antrochoanal polyp through imaging techniques, suchas CT scans, provide crucial information about its characteristic features. These scans clearly illustrate the presence of a unilateral mass originating from the maxillary sinus and extending into the nasal cavity, with its apex directed towards the choana. The accurate recognition of these key features is essential for the correct classification and coding of antrochoanal polyps according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision (ICD-10). By utilizing the appropriate ICD-10 code, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate documentation and reporting of this condition, facilitating more effective treatment planning and quality patient care.
Potential Complications
Antrochoanal polyps, classified under ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision), are abnormal growths that can cause several complications within the nasal passages. These growths often result in obstruction, leading to recurrent sinus infections and allergic reactions. Antrochoanal polyps act like a barrier, blocking the natural flow of air and secretions in the sinuses, thus creating an environment susceptible to infection and inflammation. These complications can be distressing for patients, causing chronic discomfort, difficulty breathing, and a decreased quality of life. Seeking prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment is crucial in managing antrochoanal polyps and preventing their associated complications.
If left untreated, complications arising from antrochoanal polyp, a condition characterized by the abnormal growth of polyps in the nasal cavity, can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. These complications may include symptoms like difficulty breathing, chronic sinusitis, and recurrent nasal infections. In addition to these concerns, there is a potential risk of more serious consequences such meningitis or facial abscesses. These conditions can be extremely dangerous and life-threatening if not promptly addressed. Therefore, it is crucial for patients with antrochoanal polyp to seek medical attention and appropriate treatment to prevent the progression of these complications and safeguard their overall well-being.
Antrochoanal polyps are a concerning medical condition that can lead to various complications if left untreated. These polyps have the potential to cause severe pain and inflammation within the sinuses, which can greatly impact a person’s quality of life. Additionally, intense headaches are often experienced by individuals with untreated antrochoanal polyps, making day-to-day activities challenging and disruptive. Furthermore, difficulty breathing may arise, posing additional risks and discomfort. It is crucial to address these symptoms promptly and seek proper medical attention. By following the relevant ICD-10 codes, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose and treat antrochoanal polyps, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients.
Again, it cannot be emphasized enough how crucial it is to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for antrochoanal polyps. These growths, though non-cancerous, can lead to a range of complications if left unaddressed, making it imperative that healthcare providers and benefits administrators possess reliable information regarding them. This is precisely where the ICD-10 codes prove invaluable, serving not only to aid in accurate identification and categorization of antrochoanal polyps but also to ensure efficient billing and reimbursement processes. By utilizing these codes, healthcare professionals can navigate the complex landscape of antrochoanal polyp diagnosis and treatment, ultimately striving towards optimal patient outcomes.
Treatment Options for Antrochoanal Polyp
When it comes to treating antrochoanal polyps, which are classified under ICD-10 Q43.8, the size and location of the polyp play a crucial role in determining the appropriate treatment options. Antrochoanal polyps refer to non-cancerous growths that develop in the maxillary sinus and extend into the back of the nasal cavity. These polyps can cause a range of symptoms, including nasal obstruction, chronic sinus infections, and difficulty breathing. The ICD-10 code Q43.8 specifically identifies this condition, aiding in its diagnosis and classification for medical professionals. To effectively manage antrochoanal polyps, healthcare providers must carefully consider the size and location of the polyp. Smaller polyps may be treated with conservative measures such nasal cortisone sprays or nasal saline irrigation to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. However, larger or more obstructive polyps may require surgical intervention. Surgical options can include endoscopic sinus surgery, which involves using a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera to remove the polyp through the nasal passage, or open surgical techniques for more complex cases. The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms, restore normal sinus function, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor the progress and recurrence of antrochoanal polyps. With proper assessment and an individualized approach, healthcare professionals can provide effective management for patients with this particular condition while keeping in mind the pertinent I
Antrochoanal polyp, according to the ICD-10 classification system, is a condition that can be managed with non-surgical treatments if the polyp is small and situated in a non-critical region of the nasal cavity. These treatments may involve the use of antibiotics or steroid sprays. The aim is to alleviate symptoms and provide relief without resorting to surgical intervention. By considering the specific ICD-10 code for antrochoanal polyp, healthcare professionals can identify the appropriate treatment approach for individual cases. This approach, focused on non-surgical management, is advised when dealing with antrochoanal polyps that are small and located in less critical areas of the nasal cavity. It highlights the importance of tailoring treatments to patients’ specific conditions, ensuring their well-being and minimizing the need for invasive procedures.
When it comes to antrochoanal polyps, it is important to consider the appropriate course of action for their removal. In cases where the polyps are larger or located in more critical areas, surgical intervention becomes necessary. This approach is essential to minimize the potential risks and complications associated with these polyps, such inflammation or infection. Surgical removal ensures a more thorough and effective treatment, reducing the chances of further complications. By addressing the antrochoanal polyps promptly and taking into account the specific characteristics of each case, healthcare professionals can provide patients with the appropriate care and support needed for a successful recovery.
Finally, post-surgical treatment for antrochoanal polyp ic-10 includes the administration of antibiotics in order to effectively minimize the risk of infection and prevent any future occurrence of this condition. By targeting potential sources of infection, antibiotics play a crucial role in ensuring a successful recovery process. Moreover, the use of antibiotics not only targets the immediate aftermath of surgery but also serves to prevent any potential relapses in the future. This comprehensive approach emphasizes the importance of post-surgical care in promoting the well-being and long-term health of individuals affected by antrochoanal polyp ic-10.
Prevention of Antrochoanal Polyps
Understanding the underlying causes of antrochoanal polyps is crucial in preventing their occurrence. Chronic sinus infections, allergies, asthma, and cystic fibrosis are the key factors contributing to the development of these polyps. By addressing and managing these conditions effectively, individuals can potentially reduce their risk of antrochoanal polyps. Being aware of the relationship between these medical conditions and antrochoanal polyps allows for early recognition and intervention. By adopting a proactive approach and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can work towards minimizing the chances of developing this condition. It is important to stay informed, adhere to treatment plans, and consult healthcare professionals for guidance. By doing so, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the likelihood of experiencing antrochoanal polyps.
When considering the topic of antrochoanal polyp ICD-10, it is crucial to acknowledge and understand the potential triggers that can lead to the development of this condition. By recognizing these triggers, such as smoking, environmental allergens, and microbial agents, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the chances of developing antrochoanal polyps. Smoking, for instance, has long been known to be detrimental to respiratory health and can contribute to the formation of these polyps. Similarly, exposure to environmental allergens can exacerbate symptoms and potentially lead to the development of polyps in susceptible individuals. Lastly, microbial agents, including bacteria and viruses, can play a role in the initiation or progression of antrochoanal polyps. By being aware of these potential triggers and taking appropriate measures to avoid or reduce exposure, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of developing this condition. Therefore, understanding the relationship between these triggers and antrochoanal polyp ICD-10 is crucial in promoting overall respiratory health and well-being.
Thereafter, individuals should prioritize their overall well-being by adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, as these lifestyle choices can play a pivotal role in the prevention of antrochoanal polyps. By consuming a diverse array of nutrients and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can fortify their immune system and reduce the risk of developing these polyps. Additionally, regular exercise not only helps to maintain optimal weight but also improves blood circulation and enhances overall body function, which ultimately contributes to a healthier respiratory system. By incorporating these measures into their daily routines, individuals can proactively safeguard their health and minimize the likelihood of antrochoanal polyps occurrence.
ICD-10 Coding for Antrochoanao Polyps
When coding for an antrochoanal polyp, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the specific codes provided in ICD-10 for this particular condition. The coding process requires meticulous attention to detail and accuracy to ensure proper classification and billing. Antrochoanal polyps are relatively uncommon nasal masses that typically originate from the maxillary sinus and extend into the choana, which is the posterior nasal opening. These polyps can cause symptoms such nasal obstruction, recurrent sinus infections, and even breathing difficulties in severe cases. Accurate coding is essential for documenting and tracking the prevalence of antrochoanal polyps, enabling healthcare providers to effectively monitor and manage this condition. ICD-10 codes specifically tailored for antrochoanal polyps contribute to the precise identification and appropriate classification of patients with this unique nasal pathology, aiding in accurate diagnosis and efficient management strategies. Therefore, healthcare professionals must remain up to date with the relevant ICD-10 codes to ensure proper coding, billing, and ultimately, optimal patient care.
Obtain the correct ICD-10 code is of utmost importance when it comes to accurately diagnosing antrochoanal polyps and ensuring a smooth billing process. The ICD-10 code specifically designed for antrochoanal polyps plays a vital role in accurately documenting and coding this condition. By using the designated antrochoanal polyp ICD-10 code, healthcare professionals can provide a standardized classification that facilitates effective communication and understanding among medical personnel, insurers, and researchers. This code enables healthcare providers to precisely identify and track cases of antrochoanal polyps, ensuring accurate data collection for statistical purposes. Additionally, utilizing the correct ICD-10 code for antrochoanal polyps improves the accuracy of medical records, simplifies the billing process, and promotes appropriate reimbursement for healthcare services rendered. Therefore, healthcare professionals must be well-versed in the antrochoanal polyp ICD-10 coding system to ensure optimal patient care, efficient billing processes, and accurate data analysis within the field of otolaryngology.
When it comes to the classification of antrochoanal polyps within the realm of medical coding, the two primary codes that are used are K12.4 and D12.5. These codes specifically refer to inflammatory conditions that affect the throat and the nasopharynx, respectively. The code K12.4 pertains to inflammatory conditions of the throat, while D12.5 is assigned to inflammatory conditions of the nasopharynx. These coding classifications enable healthcare professionals to accurately document and categorize antrochoanal polyps based on their specific anatomical location within the respiratory system. Utilizing these codes ensures that the recorded information is precise and comprehensive, leading to the effective management and treatment of antrochoanal polyps.
Finally, when assigning a code for an antrochoanal polyp in the ICD-10 coding protocol, it is crucial to consider other codes that may be applicable based on the patient’s medical history and the specific manifestation of the polyp. While K12.4 and D12.5 are important codes to include, they should not be the only ones considered. By thoroughly examining the patient’s medical records and taking into account any relevant codes, healthcare professionals can ensure that the ICD-10 coding accurately reflects the complexity of the condition and provides a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s diagnosis and treatment.
Alternative Treatments for Resolving Symptoms
When it comes to dealing with antrochoanal polyp symptoms, one of the best ways to ensure a safe and effective resolution is by implementing preventative measures. These measures primarily involve lifestyle changes and avoiding triggers, especially allergens. By making significant changes in our daily routines and habits, we can significantly reduce the occurrence of this condition and alleviate its symptoms. Adhering to a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate rest can boost our immune system and minimize the risk of developing antrochoanal polyps. Additionally, being mindful of our environment and taking precautions to avoid known allergens can play a crucial role in preventing the onset or recurrence of this condition. Such proactive steps can lead to a better quality of life and contribute to maintaining optimal overall health.
If these prevention methods for antrochoanal polyp ic-10 do not provide relief, alternative treatments like humidifiers or saline nasal sprays can help reduce inflammation and clear away mucus build-up that may be causing the symptoms. Antrochoanal polyp ic-10 is a condition characterized by the growth of benign polyps in the nasal cavity. These polyps can lead to symptoms such a nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, and a persistent runny nose. While prevention methods such avoiding triggers and maintaining good hygiene are important, they may not always be enough to alleviate the symptoms of this condition. In such cases, using humidifiers or saline nasal sprays can be effective in reducing inflammation and promoting the clearance of excess mucus. These alternative treatments aim to provide relief from the discomfort caused by antrochoanal polyp ic-10, helping individuals breathe easier and regain a sense of well-being.
When it comes to the treatment of antrochoanal polyp, there are various non-surgical alternatives available that can effectively help alleviate the symptoms and improve the patient’s breathing patterns. One such alternative is nasal irrigation, which involves flushing out the nasal passages with saline solution to reduce inflammation and congestion. Additionally, oral and topical antihistamines can be utilized to target and alleviate the allergic reactions associated with this condition, further reducing inflammation. In some cases, steroid medications may also be prescribed to help decrease inflammation and relieve symptoms. These non-surgical approaches provide patients with alternative options that can aid in managing their condition without resorting to surgical intervention. By incorporating these alternatives into the treatment plan, individuals with antrochoanal polyp can experience relief from symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Read also: Primary vs Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Thus, surgery remains a viable option for individuals who do not experience positive outcomes from alternative treatments such pharmacotherapy or nasal cortisone sprays in cases of antrochoanal polyp iccd-10. This procedure should be considered only after thorough consultation with a qualified physician who can assess the severity of the condition and provide personalized guidance. While surgery can offer relief and potentially resolve the symptoms associated with antrochoanal polyps, it is always crucial to seek medical expertise to ensure the best course of action is taken. By engaging in a comprehensive dialogue with a physician, patients can make informed decisions about the appropriate treatment options, ultimately leading to improved quality of life.