Hey there! Have you ever wondered why your sinuses seem to be constantly acting up? Maybe you’ve tried countless treatments, but nothing seems to provide lasting relief. Well, my friend, you’re not alone. Sinusitis, or inflammation of the sinuses, affects millions of people worldwide. But did you know that there are different types of sinusitis? In this blog post, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of chronic rhinosinusitis, specifically exploring the differences between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis. We’ll break it down in easy-to-understand terms, so you can finally get to the bottom of your sinus issues and find the right solutions. So, grab a cup of tea, sit back, and let’s unravel the mysteries of chronic rhinosinusitis together!
Introduction to Primary and Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
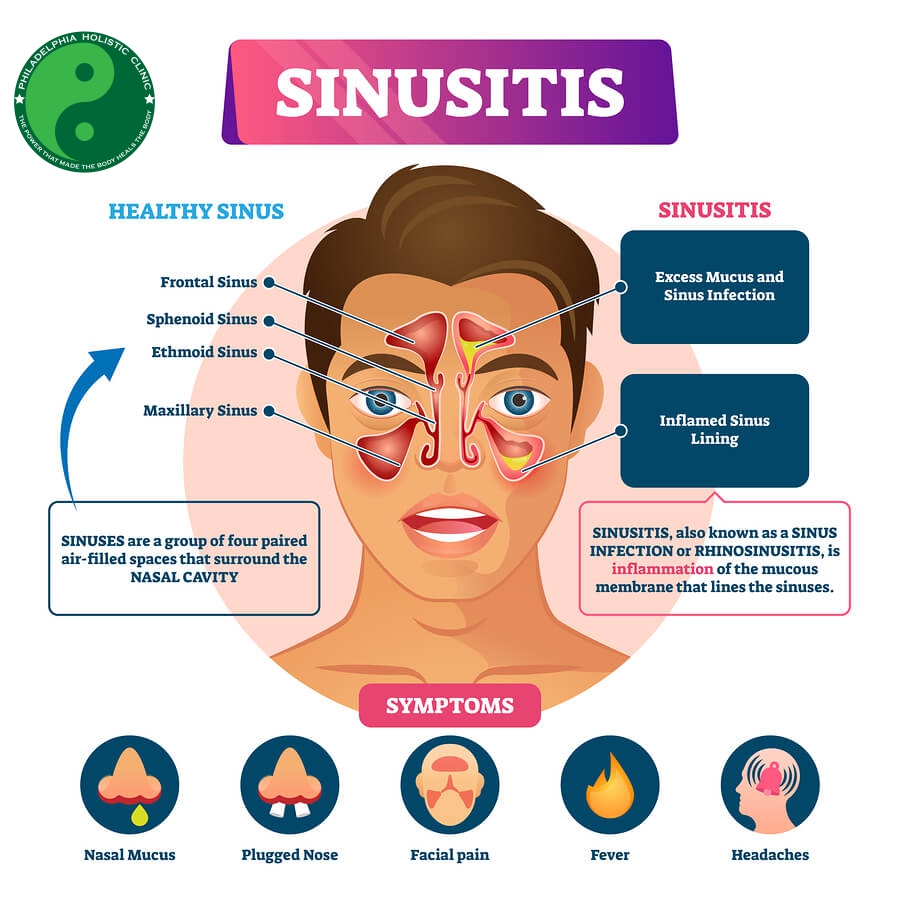
When discussing chronic rhinosinusitis, it is important to distinguish between primary and secondary cases. Primary chronic rhinosinusitis, also known as PCRS, is a prevalent medical condition characterized by long-lasting inflammation of the sinuses. This condition extends for a duration of 12 weeks or more, causing significant discomfort and impairing the overall quality of life for affected individuals. The inflammatory response within the sinuses leads to symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, difficulty breathing, and reduced sense of smell. PCRS is a result of various factors, including allergies, immune system abnormalities, nasal polyps, and anatomical abnormalities within the nose and sinuses. It is crucial to differentiate primary chronic rhinosinusitis from secondary cases, which are often associated with other underlying conditions or factors such as cystic fibrosis or immunodeficiency disorders. Understanding this distinction is essential for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and effective management of chronic rhinosinusitis to ensure optimal outcomes and relief for patients experiencing this burdensome condition.
When discussing the topic of primary versus secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, it is important to understand the distinctions between these two conditions. Secondary chronic rhinosinusitis (SCRS) refers to an inflammatory condition of the sinuses that occurs as a consequence of a previous medical condition or treatment. This condition can arise due to various factors such as allergies, cystic fibrosis, nasal polyps, and immune dysregulation. Unlike primary chronic rhinosinusitis, which may occur independently or without an identifiable cause, SCRS is directly linked to an underlying medical condition or treatment. By recognizing these differences, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage both primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis cases, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
When discussing chronic rhinosinusitis, it is important to distinguish between primary and secondary forms of the condition. PCRS (primary chronic rhinosinusitis) is the most common form, which presents with a range of symptoms. These symptoms include nasal obstruction, headache, facial pressure or pain, and purulent nasal discharge. PCRS is characterized by its chronic nature, with symptoms persisting for an extended period of time. It is essential to differentiate PCRS from secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, as the latter is often caused by other underlying conditions such as allergies, immune system disorders, or anatomical abnormalities. Understanding the distinction between primary vs secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is crucial in order to develop appropriate treatment strategies tailored to each individual’s needs.
Again, it is crucial to differentiate between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis (PCRS and SCRS) as they present with distinct symptoms and have different underlying causes. While both conditions share common signs such as nasal congestion, headache, and postnasal drip, SCRS typically has more severe symptoms, including fever and facial swelling. The presence of these additional indicators can help healthcare professionals in accurately diagnosing SCRS and ensuring appropriate treatment. By understanding the differences between PCRS and SCRS, medical practitioners can provide tailored interventions and improve the overall management of chronic rhinosinusitis, leading to better patient outcomes.
Causes of Primary and Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Primary chronic rhinosinusitis and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis represent two distinct forms of the condition. Primary chronic rhinosinusitis is primarily caused by abnormalities within the sinuses, which can include anatomic variations or immunologic disorders. These abnormalities lead to inflammation within the respiratory tract, resulting in the chronic condition. On the other hand, secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is typically a consequence of other underlying conditions, such as allergies, asthma, or nasal polyps. While both forms share the common characteristic of chronic inflammation in the sinuses, primary chronic rhinosinusitis is directly related to sinus abnormalities, whereas secondary chronic rhinosinusitis develops as a result of other pre-existing conditions. Understanding the differences between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies tailored to each patient’s specific needs.
When comparing primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, it is important to consider the various factors that contribute to the development of each condition. Secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, in particular, can arise from a range of causes including structural abnormalities, bacterial, fungal, and viral infections, allergens, inhalation of pollutants or irritants, and even autoimmunity. These factors play a significant role in the progression and severity of the sinus inflammation. Structural abnormalities can impede the normal flow of mucus, leading to a buildup and potential infection. Infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses can directly impact the sinuses and exacerbate symptoms. Allergens, such as pollen or pet dander, can trigger an immune response that results in chronic inflammation. Additionally, inhaling pollutants or irritants can irritate the sinuses and contribute to the development of rhinosinusitis. Lastly, autoimmunity, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, can also be a factor. Understanding these various contributors is crucial in differentiating between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis and determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Next, understanding the underlying causes of primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is crucial in recognizing the vast array of symptoms that can arise. From debilitating headaches and facial pressure/pain to bothersome nasal congestion/obstruction and postnasal drip, the effects of this condition can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Loss of smell/taste, fatigue, and an incessant cough only further exacerbate the distress caused by primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis. By distinguishing between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, medical professionals can tailor their treatment plans to address the specific causes and symptoms, ultimately providing patients with the utmost care and relief.
Clinical Presentation of Primary and Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Primary chronic rhinosinusitis (PCR) and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis (SCR) are two distinct types of long-term inflammation of the nasal sinuses. PCR is typically characterized by symptoms such as nasal obstruction, facial pain, and headaches. On the other hand, SCR can lead to more severe manifestations, including inflammation of the orbit or paranasal sinuses. The main difference between these two conditions lies in the presence of additional signs and symptoms in SCR cases. While PCR primarily causes discomfort in the nasal region, SCR can extend its effects to other areas of the sinus and even affect the orbit. It is important to distinguish between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis in order to provide appropriate diagnosis and treatment for patients suffering from these conditions.
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a persistent condition involving inflammation of the sinuses. Within CRS, there are two main categories: primary chronic rhinosinusitis (PCR) and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis (SCR). PCR is primarily caused by structural blockages, with nasal polyps or anatomic variations in the sinus cavities serving as common culprits. On the other hand, SCR is characterized by an underlying etiology, which can include infectious agents, allergies, or anatomical abnormalities. While PCR focuses on physical obstructions hindering sinus drainage, SCR delves into the various factors that contribute to the development of sinus inflammation. Understanding the distinction between these subtypes is crucial in formulating appropriate treatments and management strategies for individuals suffering from chronic rhinosinusitis.
Again, when comparing primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, it becomes apparent that the clinical manifestations of secondary chronic rhinosinusitis can be more severe and debilitating than those observed in primary chronic rhinosinusitis. Notably, patients with secondary chronic rhinosinusitis may experience symptoms such as fever and mucopurulent discharge from the nose or sinuses, which are often absent in primary cases. These pronounced symptoms of secondary chronic rhinosinusitis can greatly impact the overall well-being and quality of life of affected individuals. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare providers and researchers to understand and differentiate between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis to accurately diagnose, treat, and manage this condition.
Diagnosis of Primary vs Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Accurately diagnosing primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is crucial in order to effectively treat patients and optimize their outcomes. The distinction between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is of utmost importance as there are significant variations between these two conditions. Primary chronic rhinosinusitis refers to inflammation of the sinuses and nasal passages that arises without any underlying causes or predisposing factors. On the other hand, secondary chronic rhinosinusitis occurs as a result of another condition or a specific trigger, such as an infection, nasal polyps, or anatomical abnormalities. Understanding the differences between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis enables healthcare professionals to implement tailored treatment plans for each individual patient, ensuring the most appropriate interventions are provided. By accurately diagnosing and categorizing the type of chronic rhinosinusitis a patient is experiencing, healthcare providers can offer targeted therapies that address the underlying causes and alleviate symptoms more effectively.
When it comes to the distinction between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, a crucial aspect of proper diagnosis lies in ruling out any potential underlying causes. Specifically, it is essential to consider factors such as nasal polyps or allergies before diagnosing a patient with primary chronic rhinosinusitis. By carefully evaluating these possible triggers, healthcare professionals can ensure a more accurate assessment of the condition. Adhering to this approach not only helps in identifying the root cause of the symptoms but also enables appropriate and targeted treatment strategies to be implemented. Consequently, understanding and differentiating between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis play a vital role in providing effective care and improving patient outcomes.
Diagnosing chronic rhinosinusitis involves a careful evaluation of symptoms, physical examination findings, and imaging results to differentiate between primary and secondary forms of the condition. Healthcare professionals rely on a comprehensive approach that considers various factors to accurately diagnose the type of rhinosinusitis a patient may have. By thoroughly analyzing the symptoms reported by the individual, examining specific physical manifestations, and interpreting imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, medical practitioners can make an informed determination. This allows them to distinguish whether the chronic rhinosinusitis is primary, referring to cases where no underlying cause is present, or secondary, indicating an underlying condition or trigger that contributes to the sinus inflammation. Through this thorough diagnostic process, healthcare providers can effectively tailor treatment plans to address the specific needs of each patient, ensuring the most appropriate and successful outcomes for those suffering from chronic rhinosinusitis.
Furthermore, endoscopy can provide valuable insights into the differentiation between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis. By visually examining the sinuses, doctors are able to assess the extent of inflammation and identify any structural abnormalities that may contribute to the chronic condition. Additionally, endoscopy allows for the collection of tissue samples, which can be further analyzed and tested to confirm the diagnosis. This procedure plays a crucial role in distinguishing primary chronic rhinosinusitis, which is typically caused by inherent factors such as anatomical abnormalities or immune deficiencies, from secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, which may be a consequence of other underlying conditions like allergies or nasal polyps. Ultimately, the utilization of endoscopy enables doctors to provide accurate diagnoses and guide appropriate treatment plans for patients suffering from primary or secondary chronic rhinosinusitis.
Treatment Options for Primary and Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
When it comes to the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis, there are different approaches depending on whether it is primary or secondary. Primary chronic rhinosinusitis typically involves the use of medications aimed at reducing inflammation, such nasal sprays, oral corticosteroids, and antibiotics. These medications help alleviate symptoms and manage the underlying inflammation. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be required to address any obstructions that are contributing to the symptoms of primary chronic rhinosinusitis. On the other hand, secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, which is often caused by an underlying condition or an external factor, may require a different treatment approach. The treatment for secondary chronic rhinosinusitis focuses on addressing the primary condition itself, such allergy management or treating the underlying infection. In some instances, both medication and surgery may be necessary to effectively manage primary or secondary chronic rhinosinusitis. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances.
When it comes to primary versus secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, the treatment options available greatly vary depending on the underlying cause. For secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, which is often the result of an infection or inflammation, the approach typically involves the use of medications aimed at controlling the inflammation or antibiotics to treat any existing infections. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to address specific issues such a deviated septum or the presence of polyps that obstruct sinus drainage. This highlights the importance of accurately diagnosing the type of chronic rhinosinusitis one is experiencing, in order to determine the most suitable treatment path. Overall, tailoring the treatment plan to address either primary or secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is crucial in achieving long-term relief and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Next, when it comes to primary versus secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, it is crucial for patients to collaborate closely with their healthcare provider to establish a personalized treatment approach that caters to their specific requirements and aspirations for alleviating symptoms. By actively engaging in a cooperative relationship, patients can ensure that they receive the most effective and tailored treatment plan for their particular condition. Whether it is primary or secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, the goal remains the same – to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Therefore, patients should not hesitate to seek expert medical guidance and make informed decisions that will promote their overall well-being in the long term.
Prognosis for Patients with Primary and Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
When it comes to the comparison between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), primary CRS generally offers a more positive outlook. This is mainly because primary CRS tends to be less severe and easier to manage in terms of treatment. The term “primary” refers to cases where CRS develops without any underlying cause or previous medical conditions, while “secondary” CRS arises as a result of pre-existing conditions or as a complication of other medical issues. The prognosis for primary CRS is often improved due to the absence of complicating factors, which allows for a more straightforward approach to treatment. As a result, primary CRS patients typically experience milder symptoms and respond better to therapies aimed at managing the condition. In contrast, secondary CRS may be more challenging to treat, as it requires addressing the underlying cause or managing multiple medical conditions simultaneously. Therefore, understanding the distinction between primary and secondary CRS is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action for patients and achieving better outcomes.
Primary chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) refers to a condition where inflammation and swelling of the sinus and nasal passages occur without any prior sinus or nasal issues. In contrast, secondary CRS is caused by an underlying problem such a deviated septum, polyps, or allergies. When comparing the two, it is crucial to understand that secondary CRS tends to have a poorer prognosis. This is primarily because the presence of these underlying issues can complicate and make treatment more challenging. The additional factors associated with secondary CRS can make it more difficult to manage and may require a more complex treatment approach. Thus, primary CRS generally has a more favorable prognosis compared to its secondary counterpart.
Similarly, when considering the management and prognosis of primary versus secondary chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), it is important to note that aggressive treatment can greatly benefit patients in terms of symptom relief and long-term prognosis. Despite the challenges posed by both types of CRS, aggressive treatment methods targeting both the underlying causes and associated symptoms can significantly improve patients’ quality of life and overall prognosis. By addressing the underlying causes and implementing appropriate therapies, patients with both primary and secondary CRS can experience significant symptom relief and expect an improved long-term outlook. This underscores the importance of early diagnosis, prompt treatment, and a comprehensive approach to managing both primary and secondary CRS.
Differentiating Between Primary and Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Chronic Rhinosinusitis, commonly referred to by the acronym CRS, is a persistent inflammatory condition affecting the sinuses and nasal passages for a duration exceeding 12 weeks. It is crucial to understand that CRS can be categorized into two main types: primary and secondary. Primary CRS refers to cases where the inflammation occurs spontaneously without any identifiable cause or trigger. On the other hand, secondary CRS is characterized by inflammation resulting from an underlying condition or factor, such nasal polyps, deviated nasal septum, or even allergies. Distinguishing between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning. By recognizing the distinct nature of these subtypes, healthcare professionals can offer tailored management strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Primary vs secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is an important distinction when considering the etiology and pathogenesis of this condition. Primary CRS is characterized by inflammation in the sinuses due to various environmental factors like allergens, pollutants, and irritants. These external triggers can lead to chronic inflammation in the sinuses, causing symptoms such nasal congestion, facial pain and pressure, and difficulty breathing. On the other hand, secondary CRS is caused by an underlying condition that impairs sinus function. Examples of such conditions include cystic fibrosis or structural abnormalities in the nose and sinuses. These underlying factors contribute to the development of chronic rhinosinusitis by interfering with the normal drainage and ventilation of the sinuses. Understanding the distinction between primary and secondary CRS is crucial for effective diagnosis and management of this debilitating condition.
When it comes to diagnosing chronic rhinosinusitis, there are two main forms to consider – primary and secondary. The diagnosis of primary chronic rhinosinusitis primarily relies on clinical signs and symptoms exhibited by the patient. However, in the case of secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, further testing is necessary to identify the underlying cause of the condition. Both primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis share common signs and symptoms, such a facial pain or pressure, nasal obstruction or congestion, thick green or yellow nasal discharge, and loss of smell. Understanding the distinction between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is crucial in order to determine the most appropriate course of treatment for each individual patient.
Again, it is important to note that primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis differ in their underlying causes and require distinct treatment approaches. While medications such nasal corticosteroids, saline irrigation, decongestants, antibiotics, and antifungals can be effective in managing both types of CRS, the use of surgical intervention may be necessary in cases of severe or chronic secondary CRS. This involves rectifying any structural abnormalities that may be causing the condition and ultimately improving airway function. Therefore, a thorough and accurate diagnosis is crucial in order to provide patients with the most appropriate and effective treatment plan for primary vs secondary chronic rhinosinusitis.
Complications Associated With Primary and Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Primary Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a form of chronic inflammation that occurs in the sinuses without any identifiable underlying cause. This condition is characterized by persistent inflammation and is not secondary to any other health issue. Although the exact cause of primary CRS remains unknown, it is associated with several common complications, including the development of nasal polyps, frequent infections, and the formation of scar tissue within the sinus cavities. These complications can significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being and quality of life. It is important for healthcare professionals to differentiate between primary and secondary CRS in order to provide appropriate treatment and management strategies for patients. By understanding the key differences and recognizing the unique characteristics of primary CRS, healthcare providers can work towards alleviating symptoms, reducing complications, and improving patients’ long-term outcomes.
When discussing the topic of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), it is important to understand the distinction between primary and secondary CRS. Secondary CRS, in particular, is often triggered by a more severe underlying condition, such as an allergy or structural abnormality in the nose or sinuses. This distinction is crucial as secondary CRS can lead to various complications that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Some of the common complications associated with secondary CRS encompass eye problems, persistent headaches, sleep apnea, and even vision loss due to tissue damage in the sinuses. These complications not only cause discomfort but also highlight the seriousness of secondary CRS and the necessity for proper medical attention. By addressing these keywords, we can better grasp the implications of secondary CRS and the urgent need for comprehensive treatment.
Moreover, distinguishing between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Primary CRS refers to inflammation of the sinuses caused by factors such as allergies, nasal polyps, or structural abnormalities. On the other hand, secondary CRS occurs as a result of underlying conditions like cystic fibrosis, immunodeficiency disorders, or systemic diseases. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of both primary and secondary CRS are essential to minimize the risk of further complications arising from long-term chronic inflammation in the sinuses. By understanding the key differences and addressing these conditions in a timely manner, healthcare professionals can offer targeted interventions that alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent future sinus-related issues for patients with primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis.
Prevention Strategies for Patients with Primary or Secondary Chronic Rhinosinusitis
When it comes to preventing chronic rhinosinusitis, it is crucial to understand the distinctions between primary and secondary forms of the condition. Primary chronic rhinosinusitis results from inflammation of the sinus lining itself, whereas secondary chronic rhinosinusitis arises due to an underlying condition such an allergy or a structural abnormality. By recognizing these differences, individuals can take proactive steps to avoid or minimize their risk of developing chronic rhinosinusitis. Understanding whether the condition stems from inflammation or an underlying cause is essential in determining the best course of action for prevention or management. Whether primary or secondary, adopting a preventive approach can significantly enhance one’s overall sinus health and quality of life.
Primary versus secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is a topic that focuses on understanding the different causes and preventive measures for this condition. Chronic rhinosinusitis refers to long-term inflammation in the sinuses, leading to various uncomfortable symptoms. To prevent primary chronic rhinosinusitis, it is crucial to prioritize good hygiene practices and minimize exposure to potential irritants that can trigger sinus inflammation. These irritants often include cigarette smoke and dust particles, which should be avoided to maintain sinus health. Additionally, staying away from allergens such pollen or mold can significantly reduce the risk of chronic rhinosinusitis. When necessary, using a humidifier can help keep the sinuses moisturized and prevent dryness. Regularly washing hands and face with warm salt water is another effective preventive measure. By adhering to these precautions, individuals can actively safeguard themselves against primary chronic rhinosinusitis, ultimately promoting overall sinus health and well-being.
Besides identifying and treating the underlying conditions that may lead to inflammation in the sinuses, understanding the distinction between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis is crucial in providing effective management and preventing further complications. Primary chronic rhinosinusitis, typically caused by factors like allergies or structural abnormalities, necessitates targeted treatment to alleviate symptoms and minimize the risk of recurrence. However, when it comes to secondary chronic rhinosinusitis, a more comprehensive approach is required. This requires not only addressing the underlying conditions but also addressing the root cause, such an infection or immune system dysfunction. By distinguishing between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis and implementing appropriate treatments accordingly, healthcare professionals can enhance patient outcomes and ultimately improve their quality of life.
Read also: Acute Maxillary Sinusitis Recurrence Not Specified ICD 10
In conclusion, understanding the differences between primary and secondary chronic rhinosinusitis can provide valuable insights for those suffering from sinus issues. By delving into the intricacies of these conditions, we hope to have shed light on the various causes and symptoms that distinguish them from one another. Armed with this knowledge, you can now take proactive steps towards finding the right solutions and relief for your sinus problems. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and with proper understanding and guidance, you can navigate the mysteries of chronic rhinosinusitis and improve your quality of life. So, take charge of your health, explore treatment options, and breathe easy once again!